Pandas apply function to every row
Pandas is a powerful Python library used for data manipulation and analysis. One of its core functionalities is the ability to apply functions across rows or columns of a DataFrame. This article will explore the use of the apply() function to process data row-wise in a DataFrame. We will cover various scenarios where the apply() function can be utilized, providing detailed examples for each case.
Introduction to the apply() Function
The apply() function in Pandas allows users to apply a function along an axis of the DataFrame (rows or columns). When applying a function to each row, you set the axis parameter to 1. This function is extremely versatile and can be used for a wide range of data manipulation tasks, from simple arithmetic operations to more complex data transformations.
Basic Usage of apply() on Rows
Let’s start with a simple example where we apply a function to each row to calculate the sum of two columns.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Define a simple sum function
def sum_two_columns(row):
return row['A'] + row['B']
# Apply the function to each row
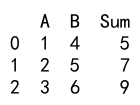
df['Sum'] = df.apply(sum_two_columns, axis=1)
print(df)
Output:
Applying Conditional Logic
You can also use apply() to implement conditional logic across rows. For example, categorizing data based on values in the rows.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Score': [88, 92, 85, 70, 60]
})
# Define a function to categorize scores
def categorize_score(row):
if row['Score'] >= 90:
return 'High'
elif row['Score'] >= 80:
return 'Medium'
else:
return 'Low'
# Apply the function to each row
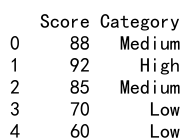
df['Category'] = df.apply(categorize_score, axis=1)
print(df)
Output:
Complex Calculations
Sometimes, you might need to perform more complex calculations that depend on multiple columns.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Price': [20, 30, 40],
'Quantity': [4, 5, 6],
'Tax': [0.2, 0.3, 0.4]
})
# Define a function to calculate total cost
def total_cost(row):
return (row['Price'] * row['Quantity']) * (1 + row['Tax'])
# Apply the function to each row
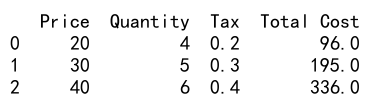
df['Total Cost'] = df.apply(total_cost, axis=1)
print(df)
Output:
Using Lambda Functions
For simpler operations, you can use lambda functions directly within the apply() method.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'X': [1, 2, 3],
'Y': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Apply a lambda function to calculate the product of two columns
df['Product'] = df.apply(lambda row: row['X'] * row['Y'], axis=1)
print(df)
Output:

Handling Text Data
Applying functions to text data is another common use case. For example, extracting domain names from email addresses.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]']
})
# Define a function to extract domain
def extract_domain(row):
return row['Email'].split('@')[1]
# Apply the function to each row
df['Domain'] = df.apply(extract_domain, axis=1)
print(df)
Output:

Advanced Data Transformations
You can also use apply() for more advanced data transformations, such as applying a series of operations.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Data': ['1,2,3', '4,5,6', '7,8,9']
})
# Define a function to calculate the average from a comma-separated string
def calculate_average(row):
numbers = list(map(int, row['Data'].split(',')))
return sum(numbers) / len(numbers)
# Apply the function to each row
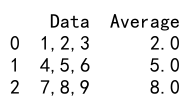
df['Average'] = df.apply(calculate_average, axis=1)
print(df)
Output:
Pandas apply function to every row Conclusion
The apply() function is a versatile tool in Pandas that allows you to apply a function to every row in a DataFrame. This can be used for a wide range of tasks from simple calculations to complex data transformations. By using the examples provided, you can start to implement the apply() function in your own data analysis tasks, enhancing your ability to manipulate and analyze data efficiently.
Remember, while apply() is powerful, it can be slower on larger datasets compared to using vectorized operations directly supported by Pandas. Always consider the size and complexity of your data when choosing your data manipulation strategies.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe