Pandas Append
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that offers a wide range of functionalities to manipulate and analyze data. One such functionality is the Pandas append method, which allows users to concatenate rows of one DataFrame to another, creating a new DataFrame in the process. This article will explore the Pandas append method in detail, providing comprehensive insights and numerous examples to demonstrate its usage.
Pandas Append Recommended Articles
- Pandas Append a Row
- Pandas Append Column
- Pandas Append Columns
- Pandas Append Columns to DataFrame
- Pandas Append Column to DataFrame
- Pandas Append DataFrame to Another
- Pandas Append DataFrame
- Pandas Append DataFrames
- Pandas Append Deprecated
- Pandas Append Row to DataFrame
- Pandas Append Row
- Pandas Append Rows to DataFrame
- Pandas Append Rows
- Pandas Append to DataFrame
- Pandas Append Two DataFrames
- Pandas Append vs Concat
Introduction to Pandas append
The Pandas append method in Pandas is used to append rows of another DataFrame to the end of the given DataFrame, returning a new DataFrame object. This method does not change the original DataFrame but returns a new DataFrame that includes the appended rows.
Syntax of Pandas append
DataFrame._append(other, ignore_index=False, verify_integrity=False, sort=False)
- other: DataFrame or Series/dict-like object, or list of these, to append.
- ignore_index: If True, the index labels are not used in the resulting DataFrame. Instead, it will be labeled as 0, 1, …, n-1.
- verify_integrity: If True, ensure that appending does not create duplicate indices.
- sort: Sort columns if the columns of
otherare not in the same order.
Basic Example of Pandas append
Here is a simple example to demonstrate the basic usage of the append method.
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2']
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A3', 'A4', 'A5'],
'B': ['B3', 'B4', 'B5']
})
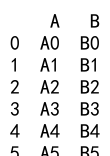
result = df1._append(df2, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Detailed Examples of Using Pandas append
Example 1: Appending Multiple DataFrames
You can append multiple DataFrames in a single operation by chaining the Pandas append method.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [30, 40]
})
df3 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [50, 60]
})
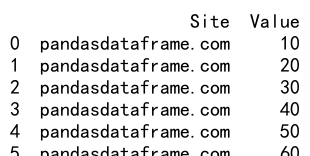
result = df1._append([df2, df3], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Example 2: Appending with Different Columns
When appending DataFrames that do not have the same columns, Pandas will automatically fill in missing values with NaN.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Page': ['Home', 'About'],
'User': [100, 200]
})
result = df1._append(df2, ignore_index=True, sort=False)
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Using verify_integrity Option
The verify_integrity option can be used to ensure that the indices in the resulting DataFrame do not have duplicates.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
}, index=[0, 1])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [30, 40]
}, index=[1, 2])
try:
result = df1._append(df2, verify_integrity=True)
print(result)
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
Output:
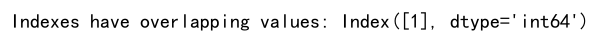
Example 4: Appending a Series as a Row
You can append a Series as a row to a DataFrame. If the Series does not have a name, it will be appended as a row in the DataFrame without an index label.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
series = pd.Series(['pandasdataframe.com', 30], index=['Site', 'Value'])
result = df._append(series, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Appending DataFrames with MultiIndex
Appending works with MultiIndex DataFrames as well.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
}).set_index(['Site', 'Value'])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [30, 40]
}).set_index(['Site', 'Value'])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:

Example 6: Appending with sort Option
The sort option allows you to sort the columns after appending if they are not aligned.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [10, 20]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': [30, 40],
'C': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
})
result = df1._append(df2, sort=True)
print(result)
Output:

Example 7: Appending Empty DataFrame
Appending an empty DataFrame will simply return the original DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame()
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:

Example 8: Appending DataFrame to Itself
You can append a DataFrame to itself to duplicate its rows.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
result = df._append(df, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Appending with Different Index Types
When appending DataFrames with different index types, the resulting DataFrame will have a mixed type index unless ignore_index=True is used.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
}, index=[0, 1])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [30, 40]
}, index=['a', 'b'])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:

Example 10: Appending with No Common Columns
When there are no common columns between the DataFrames, the resulting DataFrame will have all columns from both DataFrames, filled with NaN where necessary.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Site': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Value': [10, 20]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Page': ['Home', 'About'],
'User': [100, 200]
})
result = df1._append(df2, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:

Pandas append conclusion
The Pandas append method in Pandas is a versatile tool for combining DataFrames by adding rows. It offers options to handle indices, sort columns, and manage data integrity. By understanding and utilizing these features effectively, you can streamline your data manipulation tasks in Python. The examples provided in this article should help you get started with using Pandas append in your own projects.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe