Pandas DataFrame: Adding Columns
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that provides data structures and functions for effectively handling and analyzing data. One of the most commonly used data structures in Pandas is the DataFrame, which is a two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). In this article, we will explore various methods to add columns to a DataFrame, which is a common operation when working with data in Python.
1. Adding a New Column to a DataFrame
One of the simplest ways to add a new column to a DataFrame is by using the assignment operator (=). This method allows you to create a new column and assign it a value.
Example 1: Adding a Constant Value Column
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Add a new column with a constant value
df['Country'] = 'pandasdataframe.com'
print(df)
Output:

Example 2: Adding a Column Based on Computation from Other Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Length': [5, 6, 7],
'Width': [2, 3, 4]
})
# Add a new column by performing a calculation on existing columns
df['Area'] = df['Length'] * df['Width']
print(df)
Output:

2. Using the assign() Method
The assign() method allows you to add new columns to a DataFrame while maintaining the original DataFrame unchanged. This method is particularly useful for creating new DataFrames based on existing ones.
Example 3: Using assign() to Add a Single Column
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Temperature': [22, 24, 19],
'Humidity': [80, 70, 90]
})
# Add a new column using assign()
new_df = df.assign(FeelsLike=lambda x: x['Temperature'] * 0.9 + x['Humidity'] * 0.1)
print(new_df)
Output:

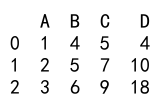
Example 4: Adding Multiple Columns Using assign()
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Add multiple new columns using assign()
new_df = df.assign(C=lambda x: x['A'] + x['B'], D=lambda x: x['A'] * x['B'])
print(new_df)
Output:
3. Inserting Columns with the insert() Method
The insert() method allows you to add a column at a specific location in the DataFrame. This method is useful when the order of columns is important.
Example 5: Inserting a Column at a Specific Index
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Insert a new column at index 1
df.insert(1, 'Country', 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(df)
Output:

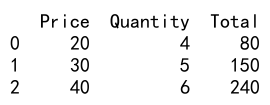
Example 6: Inserting a Column Based on Calculation
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Price': [20, 30, 40],
'Quantity': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Insert a new column at index 2
df.insert(2, 'Total', df['Price'] * df['Quantity'])
print(df)
Output:
4. Adding Columns Using Concatenation
You can also add columns to a DataFrame by concatenating it with another DataFrame or Series. This method is useful when you have data in separate structures that you want to combine.
Example 7: Concatenating a DataFrame with a Series
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Create a Series
s = pd.Series(['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'], name='Website')
# Concatenate the DataFrame and the Series
new_df = pd.concat([df, s], axis=1)
print(new_df)
Output:

Example 8: Concatenating Two DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create the first DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Create the second DataFrame
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Country': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
})
# Concatenate the two DataFrames
new_df = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1)
print(new_df)
Output:

5. Using the merge() Method
The merge() method is typically used for combining DataFrames based on one or more keys. However, it can also be used to add columns when the keys are the indices of the DataFrames.
Example 9: Using merge() to Add Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create the first DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Create the second DataFrame
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Country': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}, index=[0, 1, 2])
# Merge the two DataFrames
new_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, left_index=True, right_index=True)
print(new_df)
Output:

6. Adding Columns from Another DataFrame Based on a Key
Sometimes, you may want to add columns from one DataFrame to another based on a matching key. This can be achieved using the merge() method with a specified key.
Example 10: Adding Columns Based on a Key
import pandas as pd
# Create the first DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Create the second DataFrame
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Country': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
})
# Merge the two DataFrames based on the 'Name' column
new_df = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Name')
print(new_df)
Output:

Pandas dataframe add column conclusion
Adding columns to a DataFrame is a common operation in data manipulation and analysis. In this article, we explored several methods to add columns to a Pandas DataFrame, including using assignment, the assign() method, the insert() method, concatenation, and the merge() method. Each method has its own use cases and advantages, and understanding these can help you effectively manipulate data using Pandas.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe