Pandas Concat Series
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that offers various functionalities for data analysis and manipulation. One of the key operations in data manipulation is the concatenation of data structures. In this article, we will explore how to concatenate Series objects using the Pandas library. We will cover different scenarios and provide detailed examples to help you understand and apply these techniques in your data projects.
Introduction to Pandas Series
A Pandas Series is a one-dimensional array-like object that can hold data of any type (integers, strings, floating points, Python objects, etc.). It is capable of holding axis labels, collectively known as an index. The basic method to create a Series is to call:
import pandas as pd
data = [1, 2, 3, 4]
series = pd.Series(data)
print(series)
Output:

Concatenating Series
Concatenation is the process of appending one or more Series to another Series. The concat() function in Pandas is used for this purpose. It can concatenate along a particular axis (rows or columns) and is very versatile with various parameters to control the concatenation operation.
Basic Concatenation of Two Series
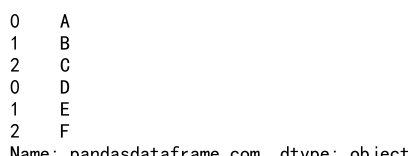
Here is the simplest form of concatenation, combining two Series end-to-end:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series(['A', 'B', 'C'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series(['D', 'E', 'F'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2])
print(result)
Output:
Concatenation with Index Continuity
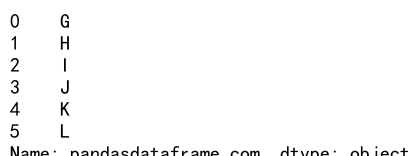
If you want the resulting Series to maintain a continuous index, you can use the ignore_index parameter:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series(['G', 'H', 'I'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series(['J', 'K', 'L'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Concatenating Series with Different Indices
When Series have different indices, you can still concatenate them:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series(['M', 'N'], index=[1, 2], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series(['O', 'P'], index=[3, 4], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2])
print(result)
Output:

Using MultiIndex
You can create a hierarchical index (MultiIndex) by specifying the keys parameter:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series(['Q', 'R'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series(['S', 'T'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], keys=['first', 'second'])
print(result)
Output:

Concatenation Along Axis=1
Concatenating Series side by side (forming a DataFrame) using axis=1:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([1, 2], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series([3, 4], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

Handling Series with Different Lengths
When Series of different lengths are concatenated, missing values are filled with NaN:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([5, 6, 7], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series([8, 9], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:

Concatenation with Mixed Data Types
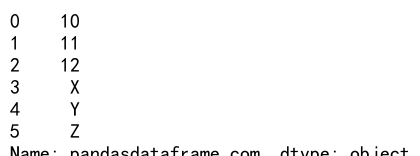
Concatenating Series containing different data types:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([10, 11, 12], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series(['X', 'Y', 'Z'], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Using Append Method
The append() method is a shortcut to concat() specifically for appending Series or DataFrame objects:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([13, 14, 15], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series([16, 17, 18], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = s1.append(s2, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Concatenation with Custom Index Names
Setting custom index names after concatenation:
import pandas as pd
s1 = pd.Series([19, 20, 21], name='pandasdataframe.com')
s2 = pd.Series([22, 23, 24], name='pandasdataframe.com')
result = pd.concat([s1, s2], keys=['Series1', 'Series2'])
result.index.names = ['Source', 'Row']
print(result)
Output:

Pandas Concat Series Conclusion
Concatenating Series in Pandas is a straightforward yet powerful operation that can be tailored to fit various data manipulation needs. By understanding and utilizing the parameters of the concat() function, you can efficiently combine Series objects to form larger datasets, handle missing data, and align data according to your requirements. The examples provided in this article should serve as a foundation for your data manipulation tasks using Pandas.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe