Pandas loc and iloc
Pandas is a powerful Python library used for data manipulation and analysis. It provides numerous functionalities that make it easy to clean, analyze, and visualize data. Two of the most useful functionalities provided by Pandas are loc and iloc for data selection. This article will delve into the details of these two functions, providing a comprehensive guide on how to use them effectively in various scenarios.
Understanding loc
The loc attribute is used to access a group of rows and columns by labels or a boolean array. loc primarily works with the labels of the index or column names.
Basic Usage of loc
Here is an example of how to use loc to select a single row from a DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[0])
Output:

Selecting Multiple Rows
loc can also be used to select multiple rows. Here’s how you can select multiple specific rows:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[[0, 2]])
Output:

Selecting Rows with a Condition
You can use loc to select rows based on a condition. Here’s an example:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[df['Age'] > 25])
Output:
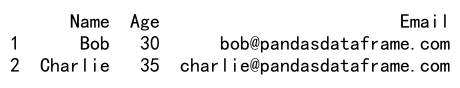
Selecting Specific Columns
With loc, you can specify the columns you want to select:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[:, ['Name', 'Email']])
Output:

Combining Conditions
You can combine conditions to make more complex queries:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[(df['Age'] > 25) & (df['Name'] == 'Charlie')])
Output:
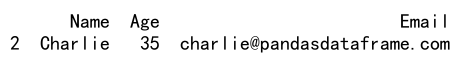
Understanding iloc
The iloc attribute is used to access a group of rows and columns by integer position(s). iloc is integer-based, so you specify rows and columns by their integer position.
Basic Usage of iloc
Here is how you can use iloc to select the first row of a DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[0])
Output:

Selecting Multiple Rows
iloc can select multiple rows by passing a list of row indices:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[[0, 2]])
Output:

Selecting Specific Columns
You can select specific columns by their integer position:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[:, [0, 2]])
Output:

Slicing Rows and Columns
You can slice both rows and columns with iloc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[0:2, 0:2])
Output:

Selecting Rows and Columns Simultaneously
With iloc, you can select specific rows and columns simultaneously:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[[0, 2], [1, 2]])
Output:

Practical Examples Combining loc and iloc
Updating Data
You can update data in a DataFrame using both loc and iloc. Here’s an example using loc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.loc[0, 'Age'] = 26
print(df)
Output:
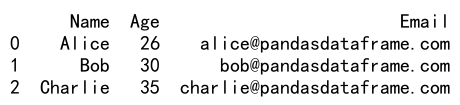
And here’s how you can do it with iloc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.iloc[0, 1] = 27
print(df)
Output:
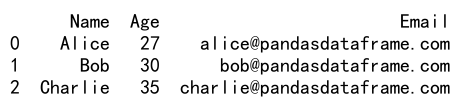
Deleting Rows
To delete rows using loc, you can use a condition:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df = df.loc[df['Age'] > 25]
print(df)
Output:
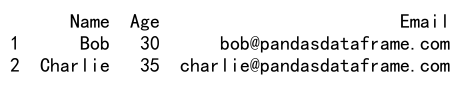
Adding a New Column
You can add a new column using loc like this:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.loc[:, 'Location'] = 'Unknown'
print(df)
Output:

Complex Conditions
Handling complex conditions with loc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.loc[(df['Age'] > 25) | (df['Name'].str.contains('Bob'))])
Output:
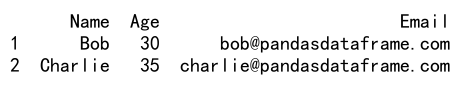
Using iloc with Functions
You can use iloc alongside functions to perform operations. For example, to get the last two rows:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.iloc[-2:])
Output:
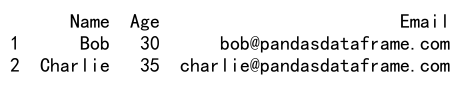
Pandas loc and iloc Conclusion
The loc and iloc functions in Pandas provide robust capabilities for data selection and manipulation. By understanding how to use these tools effectively, you can handle a wide range of data processing tasks more efficiently. Whether you are filtering data, selecting specific elements, or modifying a DataFrame, loc and iloc are indispensable tools in the arsenal of any data scientist or analyst working with Python.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe