Pandas astype int64
Pandas is a powerful and flexible open-source data analysis and manipulation library for Python. It provides data structures and functions needed to work on structured data seamlessly. One of the most common tasks in data manipulation is converting data types. In this article, we will focus on converting data types to int64 using the astype method in Pandas. We will explore various scenarios and provide detailed examples to illustrate the usage of astype for converting data types to int64.
1. Introduction to astype Method
The astype method in Pandas is used to cast a pandas object to a specified data type. This method is very flexible and can be used to convert columns of a DataFrame to different data types, including int64. The syntax for the astype method is as follows:
DataFrame.astype(dtype, copy=True, errors='raise')
dtype: Data type to which the object is to be cast.copy: Whether to return a copy (default is True).errors: Control raising of exceptions on invalid data for provided dtype. Options are ‘raise’, ‘ignore’.
2. Converting Single Column to int64
To convert a single column in a DataFrame to int64, you can use the astype method and specify int64 as the target data type.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Convert column 'A' to int64
df['A'] = df['A'].astype('int64')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
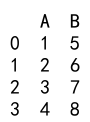
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’.
- Column ‘A’ contains float values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert column ‘A’ toint64.
3. Converting Multiple Columns to int64
To convert multiple columns in a DataFrame to int64, you can use the astype method and specify a dictionary with column names as keys and int64 as values.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8'],
'C': [9.9, 10.1, 11.2, 12.3]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'C' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'C': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
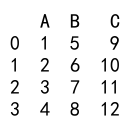
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’.
- Columns ‘A’ and ‘C’ contain float values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘C’ toint64.
4. Handling Missing Values
When converting columns with missing values (NaNs) to int64, you need to handle the missing values appropriately, as int64 does not support NaNs.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a DataFrame with missing values
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Fill missing values with a placeholder and convert to int64
df['A'] = df['A'].fillna(0).astype('int64')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
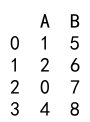
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’.
- Column ‘A’ contains float values and a missing value (NaN).
- We fill the missing value with 0 using the
fillnamethod and then convert column ‘A’ toint64.
5. Converting DataFrame with Mixed Data Types
When dealing with a DataFrame that has mixed data types, you can selectively convert specific columns to int64.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8'],
'C': [True, False, True, False]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:

Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’.
- Column ‘A’ contains float values, column ‘B’ contains string values, and column ‘C’ contains boolean values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
6. Converting Object Type Columns to int64
Object type columns often contain string representations of numbers. You can convert these columns to int64 using the astype method.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with object type columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
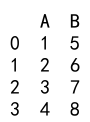
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
7. Converting Float Columns to int64
Float columns can be converted to int64 using the astype method. This conversion will truncate the decimal part.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with float columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': [5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
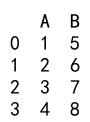
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing float values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
8. Converting Boolean Columns to int64
Boolean columns can be converted to int64 using the astype method. True will be converted to 1 and False will be converted to 0.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with boolean columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [True, False, True, False],
'B': [False, True, False, True]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
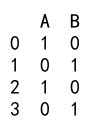
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing boolean values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
9. Converting String Columns to int64
String columns that contain numeric values can be converted to int64 using the astype method.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with string columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
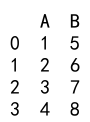
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
10. Error Handling in Type Conversion
When converting data types, you may encounter errors if the data cannot be converted to the specified type. You can handle these errors using the errors parameter.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'three', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', 'seven', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64 with error handling
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'}, errors='ignore')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:

Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers and non-numeric strings.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64witherrors='ignore'to handle conversion errors gracefully.
11. Practical Examples
Example 1: Converting a DataFrame with Mixed Data Types
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8'],
'C': [True, False, True, False],
'D': ['9', '10', '11', '12']
})
# Convert columns 'A', 'B', and 'D' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64', 'D': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:

Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, and ‘D’ containing mixed data types.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘D’ toint64.
Example 2: Handling Missing Values in Conversion
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a DataFrame with missing values
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Fill missing values with a placeholder and convert to int64
df['A'] = df['A'].fillna(0).astype('int64')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
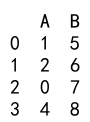
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing float values and a missing value (NaN).
- We fill the missing value with 0 using the
fillnamethod and then convert column ‘A’ toint64.
Example 3: Converting Object Type Columns to int64
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with object type columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
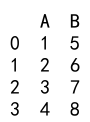
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
Example 4: Converting Float Columns to int64
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with float columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': [5.5, 6.6, 7.7, 8.8]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
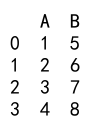
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing float values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
Example 5: Converting Boolean Columns to int64
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with boolean columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [True, False, True, False],
'B': [False, True, False, True]
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
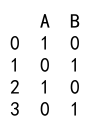
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing boolean values.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
Example 6: Converting String Columns to int64
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with string columns
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
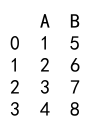
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64.
Example 7: Error Handling in Type Conversion
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'three', '4'],
'B': ['5', '6', 'seven', '8']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to int64 with error handling
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64'}, errors='ignore')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:

Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing string representations of numbers and non-numeric strings.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ toint64witherrors='ignore'to handle conversion errors gracefully.
Example 8: Converting a DataFrame with Mixed Data Types
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, 3.3, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8'],
'C': [True, False, True, False],
'D': ['9', '10', '11', '12']
})
# Convert columns 'A', 'B', and 'D' to int64
df = df.astype({'A': 'int64', 'B': 'int64', 'D': 'int64'})
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:

Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’, ‘B’, ‘C’, and ‘D’ containing mixed data types.
- We use the
astypemethod to convert columns ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘D’ toint64.
Example 9: Handling Missing Values in Conversion
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a DataFrame with missing values
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4],
'B': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
})
# Fill missing values with a placeholder and convert to int64
df['A'] = df['A'].fillna(0).astype('int64')
# Print the DataFrame
print(df)
Output:
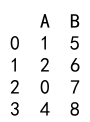
Explanation:
- We create a DataFrame with columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ containing float values and a missing value (NaN).
- We fill the missing value with 0 using the
fillnamethod and then convert column ‘A’ toint64.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe