Pandas astype with NaN
Introduction
In the world of data manipulation and analysis, the pandas library stands out as a powerful tool. One common challenge when working with pandas is handling missing data, often represented as NaN (Not a Number). This article will delve into how the astype method in pandas can be used effectively when dealing with NaN values. We will explore various scenarios and provide detailed examples to illustrate how astype interacts with NaN values. Each code snippet will be fully self-contained and designed to be run independently.
1. Overview of astype Method
The astype method in pandas is used to cast a pandas object to a specified dtype (data type). This is particularly useful for ensuring that your data is in the correct format for analysis or visualization. The syntax for astype is straightforward:
DataFrame.astype(dtype, copy=True, errors='raise')
dtype: Data type to which you want to cast the DataFrame or Series.copy: By default,True, which means a new DataFrame or Series is returned.errors: If set to ‘raise’, it will raise an error if the conversion fails. If set to ‘ignore’, it will not raise an error.
2. Handling NaN Values
NaN values can pose a significant challenge when converting data types. In pandas, NaN is a special floating-point value that is used to denote missing values. When converting data types, it is crucial to understand how NaN values are handled to avoid unexpected results.
3. Converting Data Types with NaN
When using the astype method, NaN values are typically preserved. However, the ability to convert a column containing NaN values to another data type depends on the target data type. Below are some detailed examples demonstrating various scenarios:
Example 1: Converting object to float with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1.1', '2.2', 'NaN', '4.4'],
'B': ['5.5', 'NaN', '7.7', '8.8']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Converting column 'A' from object to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles NaN by interpreting the string 'NaN' as np.nan.
Output:

Explanation
Here, we start with a DataFrame where NaN values are represented as strings. We replace these strings with np.nan and then convert the column to float.
4. Ensuring Data Integrity
When converting data types, it is crucial to ensure that the conversion does not compromise the integrity of your data. For instance, converting a string representation of dates to datetime objects should be done carefully to avoid incorrect date parsing.
Example 2: Converting object to datetime with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'date': ['2021-01-01', '2021-02-02', 'NaN', '2021-04-04']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Converting column 'date' from object to datetime
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], errors='coerce')
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles NaN by using pd.to_datetime with errors='coerce', which converts invalid parsing to NaT.
Output:

Explanation
In this example, we demonstrate how to convert a column containing date strings and NaN values to datetime objects. The errors='coerce' parameter ensures that any invalid parsing results in NaT (Not a Time), which is pandas’ equivalent of NaN for datetime objects.
Example 3: Converting float to string with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4],
'B': [5.5, np.nan, 7.7, 8.8]
})
# Converting column 'A' from float to string
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(str)
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles NaN by converting it to the string 'nan'.
Output:

Explanation
Here, we convert a column of float values (including NaN) to strings. NaN is converted to the string 'nan'.
5. Real-World Scenarios
Scenario 1: Financial Data with Missing Values
In financial datasets, missing values are common. Let’s see how to handle a scenario where we need to convert columns to different types while dealing with NaN values.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'date': ['2021-01-01', '2021-02-02', 'NaN', '2021-04-04'],
'price': ['100.5', 'NaN', '200.1', '150.0'],
'volume': ['1000', 'NaN', '500', '750']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Converting columns to appropriate types
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date'], errors='coerce')
df['price'] = df['price'].astype(float)
df['volume'] = df['volume'].astype('Int64')
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This scenario demonstrates handling multiple types with NaN values, ensuring data integrity.
Output:
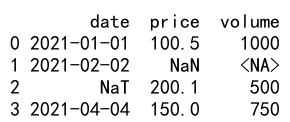
Explanation
In this real-world scenario, we handle a financial dataset with columns for dates, prices, and volumes. We ensure each column is converted to its appropriate type while correctly handling NaN values.
6. Practical Examples
Example 4: Converting float to bool with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.0, 0.0, np.nan, 4.0]
})
# Converting column 'A' from float to bool
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(bool)
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion interprets NaN as False in boolean context.
Output:

Explanation
This example shows how to convert a column of floats to booleans. NaN values are interpreted as False.
Example 5: Converting object to category with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['dog', 'cat', 'NaN', 'bird']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Converting column 'A' from object to category
df['A'] = df['A'].astype('category')
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles NaN by preserving it in the category dtype.
Output:

Explanation
Here, we convert a column of strings (including NaN) to a categorical type. NaN values are preserved.
Example 6: Converting float to complex with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4]
})
# Converting column 'A' from float to complex
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(complex)
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion preserves NaN values in the complex dtype.
Output:
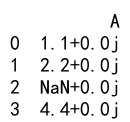
Explanation
This example demonstrates converting a column of floats to complex numbers. NaN values are preserved as complex NaN.
Example 7: Converting object to int with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'NaN', '4']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Converting column 'A' from object to Int64
df['A'] = df['A'].astype('Int64')
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion uses nullable Int64 dtype to handle NaN.
Output:
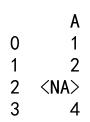
Explanation
In this example, we convert a column of strings (including NaN) to integers using the nullable Int64 dtype.
Example 8: Converting float to string and handling NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1.1, 2.2, np.nan, 4.4],
'B': [5.5, np.nan, 7.7, 8.8]
})
# Converting column 'A' from float to string
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(str)
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles NaN by converting it to the string 'nan'.
Output:

Explanation
Here, we convert a column of float values (including NaN) to strings. NaN is converted to the string 'nan'.
Example 9: Converting object to float with mixed types
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Creating a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1.1', 'two', 'NaN', '4.4']
})
# Replacing 'NaN' with actual np.nan
df.replace('NaN', np.nan, inplace=True)
# Attempting to convert column 'A' from object to float
df['A'] = pd.to_numeric(df['A'], errors='coerce')
print(df)
# Output should include `pandasdataframe.com` in comments
# This conversion handles invalid parsing with errors='coerce', converting them to NaN.
Output:

Explanation
In this example, we attempt to convert a column containing both valid and invalid float strings to floats. The errors='coerce' parameter ensures that any invalid parsing results in NaN.
7. Summary
Handling NaN values when converting data types in pandas is a crucial skill for any data analyst or scientist. The astype method offers a powerful way to ensure your data is in the correct format, but it requires careful consideration of NaN values to maintain data integrity. Through the examples provided, we have seen various scenarios and solutions for dealing with NaN values across different data types. Whether converting to integers, floats, strings, or more complex types like datetime and categories, understanding how to manage NaN values will enhance your ability to work effectively with pandas.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe