Iterate Through Pandas Series
Iterating through a Pandas Series is a common task in data analysis and manipulation. Pandas provides several methods to efficiently iterate over the elements of a Series. This article will explore various ways to iterate through a Pandas Series, including using loops, apply functions, and vectorized operations. Each method will be demonstrated with detailed example code snippets.
1. Using Simple For Loop
The simplest way to iterate through a Series is using a for loop. This method is straightforward but not always the most efficient, especially for large datasets.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'], index=['a', 'b', 'c'])
# Iterate using a for loop
for item in data:
print(f"Item: {item} from pandasdataframe.com")
Output:

2. Using iteritems() Method
The iteritems() method allows you to iterate through the Series, returning both the index and the value. This is more efficient than a simple for loop.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([10, 20, 30], index=['x', 'y', 'z'])
# Iterate using iteritems()
for index, value in data.iteritems():
print(f"Index: {index}, Value: {value} from pandasdataframe.com")
3. Using apply() Function
The apply() function is used to apply a function along the input axis of the DataFrame. It is highly efficient for applying complex operations across series elements.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3])
# Define a custom function
def custom_function(x):
return x * 10
# Apply function
result = data.apply(custom_function)
print(result)
Output:

4. Using Vectorized Operations
Vectorized operations are the most efficient way in Pandas and should be used whenever possible. These operations apply a function to all elements of a series simultaneously.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4])
# Perform vectorized addition
result = data + 10
print(result)
Output:

5. Using map() Function
The map() function is used to map values of a Series according to an input mapping or function. This is useful for transforming data elements based on a dictionary mapping or a function.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series(['red', 'blue', 'green'])
# Map using a dictionary
color_map = {'red': '#FF0000', 'blue': '#0000FF', 'green': '#00FF00'}
result = data.map(color_map)
print(result)
Output:

6. Using filter() Function
The filter() function is used to filter elements of a Series based on a defined criterion. This is useful for extracting elements that meet certain conditions.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series(range(10))
# Filter even numbers
result = data.filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
print(result)
7. Using List Comprehension
List comprehension provides a concise way to create lists and can be used to iterate through a Series. It is often more readable and concise than a for loop.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Using list comprehension to square each element
squares = [x**2 for x in data]
print(squares)
Output:
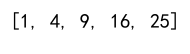
8. Using groupby() Method
The groupby() method is used to group large amounts of data and compute operations on these groups. This is useful in data aggregation tasks.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series(['apple', 'banana', 'apple', 'cherry'], index=[1, 2, 1, 2])
# Group by values
grouped = data.groupby(data.values)
# Print groups
for name, group in grouped:
print(f"Group: {name} from pandasdataframe.com, Elements: {list(group)}")
Output:

9. Using explode() Method
The explode() method is used to transform each element of a list-like to a row, replicating the index values. This is useful when working with Series containing lists.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
# Explode the series
result = data.explode()
print(result)
Output:

10. Using where() Method
The where() method is used to replace values where the condition is False. This is useful for conditional operations within a Series.
import pandas as pd
# Create a Pandas Series
data = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
# Conditionally replace values
result = data.where(data > 3, other='Less than 4 from pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

These examples demonstrate various ways to iterate through a Pandas Series, each suited for different scenarios and requirements in data processing and analysis. By choosing the appropriate method, you can ensure efficient and effective handling of data within a Pandas Series.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe