Pandas DataFrame: loc and iloc
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that provides data structures and functions for effectively handling and analyzing large datasets. Among its core features, the DataFrame object is particularly important. It is a two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). In this article, we will delve deep into two primary methods used for data selection in Pandas DataFrames: loc and iloc.
Understanding loc and iloc
loc and iloc are indexing operators that are used for different types of selections: by label (loc) and by integer location (iloc). These functions enable precise and efficient selection of data from a DataFrame.
loc: Label-based Selection
The loc method allows selection by labels of the index. It can accept a single label, a list of labels, or a slice of labels. Here are some key points about loc:
– It selects rows and columns with specific labels.
– It can also be used with boolean arrays.
iloc: Integer Position-based Selection
The iloc method is used for selection by integer position. Like loc, it can take a single integer, a list of integers, or a slice of integers. Here are some key points about iloc:
– It selects rows and columns by integer positions.
– It is similar to Python list slicing.
Examples of Using loc and iloc
Let’s explore some examples to understand how loc and iloc can be used in different scenarios. Each example will be a standalone snippet that can be directly run in a Python environment with Pandas installed.
Example 1: Basic Usage of loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[0]
print(result)
Output:

Example 2: Selecting Multiple Rows with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[[0, 2]]
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Selecting Rows by Slice with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[0:1]
print(result)
Output:

Example 4: Selecting Columns with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[:, 'Website']
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Selecting Rows and Columns with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[0, 'Website']
print(result)
Output:

Example 6: Boolean Indexing with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.loc[df['Visits'] > 900]
print(result)
Output:

Example 7: Setting Values with loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.loc[0, 'Visits'] = 1100
print(df)
Output:

Example 8: Basic Usage of iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.iloc[0]
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Selecting Multiple Rows with iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.iloc[[0, 2]]
print(result)
Output:

Example 10: Selecting Rows by Slice with iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.iloc[0:2]
print(result)
Output:

Example 11: Selecting Columns with iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.iloc[:, 1]
print(result)
Output:

Example 12: Selecting Rows and Columns with iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
result = df.iloc[0, 1]
print(result)
Output:
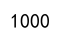
Example 13: Setting Values with iloc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'example.com', 'testsite.com'],
'Visits': [1000, 1500, 800]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df.iloc[0, 1] = 1200
print(df)
Output:

Pandas DataFrame: loc and iloc Conclusion
In this article, we explored the loc and iloc methods of Pandas DataFrames, which are essential for data selection and manipulation. Through a series of examples, we demonstrated how these methods can be used to select and modify data based on label and integer position. Understanding these methods is crucial for anyone working with data in Python, as they provide the means to efficiently and accurately access and modify data within a DataFrame.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe