Pandas Append DataFrame
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that offers a wide range of functionalities for data analysis and manipulation. One of the common operations when working with data is appending one DataFrame to another. Appending data is a critical operation in data preparation and analysis, especially when you need to combine data from multiple sources or for incremental data aggregation. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to use the append() function in pandas, complete with detailed examples.
Understanding DataFrame Append
The append() function in pandas is used to concatenate two or more pandas DataFrames along the rows. This function returns a new DataFrame by adding the rows of the second DataFrame to the first DataFrame. It is important to note that the append() function does not change the original DataFrames; instead, it returns a new DataFrame that is the result of the operation.
Syntax of append()
The basic syntax of the append() function is as follows:
DataFrame.append(other, ignore_index=False, verify_integrity=False, sort=False)
other: The DataFrame or Series/dict-like object to append to the caller.ignore_index: If True, the resulting axis will be labeled 0, 1, …, n – 1. Default is False.verify_integrity: If True, raise ValueError on creating index with duplicates.sort: Sort columns if the columns ofselfandotherare not aligned.
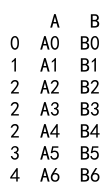
Example 1: Basic Append Operation
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
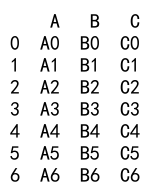
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
Example 2: Append with ignore_index
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
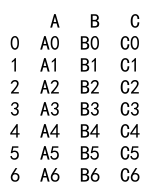
result = df1._append(df2, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Example 3: Append with Column Mismatch
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with different columns
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
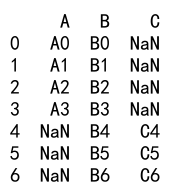
result = df1._append(df2, sort=True)
print(result)
Output:
Example 4: Append Using a Series as other
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a Series
s = pd.Series(['A4', 'B4', 'C4'], index=['A', 'B', 'C'])
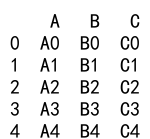
result = df._append(s, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
Example 5: Append Multiple DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create three DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
df3 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A8', 'A9', 'A10', 'A11'],
'B': ['B8', 'B9', 'B10', 'B11'],
'C': ['C8', 'C9', 'C10', 'C11']
}, index=[8, 9, 10, 11])
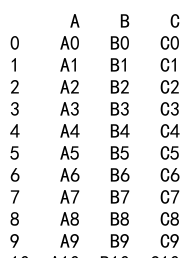
result = df1._append([df2, df3])
print(result)
Output:
Advanced Append Operations
Example 6: Append with Verification of Integrity
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with potential overlapping indexes
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[3, 4, 5, 6]) # Note the overlapping index
try:
result = df1._append(df2, verify_integrity=True)
print(result)
except ValueError as e:
print("ValueError:", e)
Output:
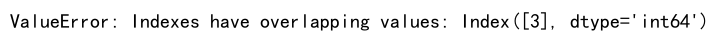
Example 7: Append DataFrames with Different Column Orders
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with different column orders
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7'],
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
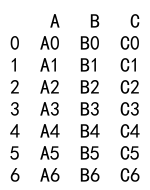
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
Example 8: Append with Non-Aligning Columns and sort=False
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with non-aligning columns
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7'],
'D': ['D4', 'D5', 'D6', 'D7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
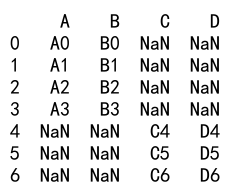
result = df1._append(df2, sort=False)
print(result)
Output:
Example 9: Append with a Dictionary
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a dictionary to append
data_dict = {'A': 'A4', 'B': 'B4', 'C': 'C4'}
result = df._append(data_dict, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
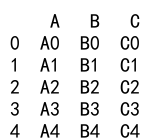
Example 10: Append with Different DataTypes
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with different data types
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'B': [5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0]
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['9', '10', '11', '12'],
'B': ['13.0', '14.0', '15.0', '16.0']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
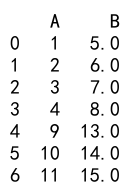
Example 11: Append with MultiIndex DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with MultiIndex
arrays = [['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'], ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Data1': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'Data2': [5, 6, 7, 8]
}, index=index)
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Data1': [9, 10, 11, 12],
'Data2': [13, 14, 15, 16]
}, index=index)
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
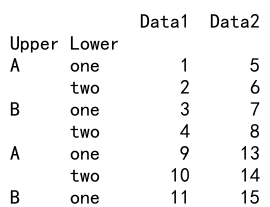
Example 12: Append with Non-unique Index
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with non-unique indexes
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 2])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=[2, 3, 4, 5])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
Example 13: Append with a DataFrame and Series with Different Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a Series with different columns
s = pd.Series(['C4', 'D4'], index=['C', 'D'])
result = df._append(s, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:

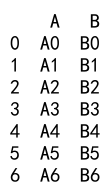
Example 14: Append DataFrames with Custom Index Names
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with custom index names
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=pd.Index([0, 1, 2, 3], name='Row'))
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=pd.Index([4, 5, 6, 7], name='Row'))
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
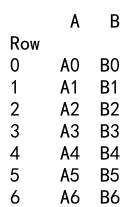
Example 15: Append with DataFrame and Series with Same Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a Series with the same columns
s = pd.Series(['A4', 'B4'], index=['A', 'B'])
result = df._append(s, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
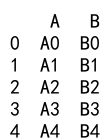
Example 16: Append with DataFrame and Series with Index
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a Series with an index
s = pd.Series(['A4', 'B4'], index=['A', 'B'])
result = df._append(s, ignore_index=True)
print(result)
Output:
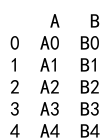
Example 17: Append DataFrames with Different Index Levels
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames with different index levels
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=pd.Index([0, 1, 2, 3], name='Level1'))
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=pd.Index([4, 5, 6, 7], name='Level2'))
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
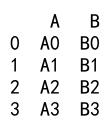
Example 18: Append with DataFrame and None
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Append None
result = df._append(None)
print(result)
Output:
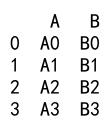
Example 19: Append with DataFrame and Empty DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create an empty DataFrame
empty_df = pd.DataFrame()
result = df._append(empty_df)
print(result)
Output:
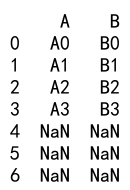
Example 20: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with No Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a DataFrame with no columns and some rows
empty_columns_df = pd.DataFrame(index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
result = df._append(empty_columns_df)
print(result)
Output:
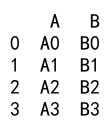
Example 21: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with No Rows
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create a DataFrame with columns but no rows
no_rows_df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['A', 'B'])
result = df._append(no_rows_df)
print(result)
Output:
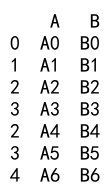
Example 22: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with Different Column Order
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create another DataFrame with the same columns but in a different order
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
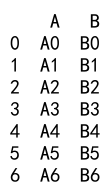
Example 23: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with Additional Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create another DataFrame with additional columns
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7'],
'C': ['C4', 'C5', 'C6', 'C7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
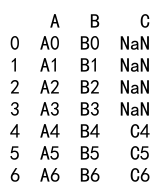
Example 24: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with Missing Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3'],
'C': ['C0', 'C1', 'C2', 'C3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create another DataFrame missing one column
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=[4, 5, 6, 7])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
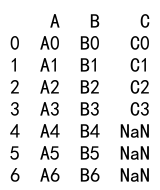
Example 25: Append with DataFrame and DataFrame with Overlapping Indexes
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A0', 'A1', 'A2', 'A3'],
'B': ['B0', 'B1', 'B2', 'B3']
}, index=[0, 1, 2, 3])
# Create another DataFrame with overlapping indexes
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['A4', 'A5', 'A6', 'A7'],
'B': ['B4', 'B5', 'B6', 'B7']
}, index=[2, 3, 4, 5])
result = df1._append(df2)
print(result)
Output:
These examples illustrate various scenarios of appending DataFrames using the append method in pandas, demonstrating how it handles different data structures, index configurations, and column setups.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe