Pandas Append Columns
Pandas is a powerful Python library used for data manipulation and analysis. One of the common tasks in data analysis is appending columns to an existing DataFrame. This can be useful in various scenarios, such as adding new features, results of computations, or merging data from different sources. In this article, we will explore different methods to append columns to a DataFrame using Pandas, providing detailed examples for each method.
1. Using the assign Method
The assign method is a straightforward way to add new columns to a DataFrame. It returns a new DataFrame with the new columns added to the old DataFrame.
Example 1: Adding a Single Column
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Append a new column
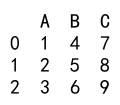
df_new = df.assign(C=[7, 8, 9])
print(df_new)
Output:
Example 2: Adding Multiple Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Append multiple new columns
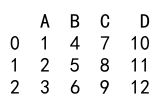
df_new = df.assign(C=[7, 8, 9], D=[10, 11, 12])
print(df_new)
Output:
2. Using the [] Operator
You can also use the [] operator to add new columns to a DataFrame. This method modifies the original DataFrame in place.
Example 3: Adding a Single Column
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Append a new column
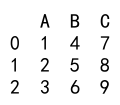
df['C'] = [7, 8, 9]
print(df)
Output:
Example 4: Adding Multiple Columns Using a Loop
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
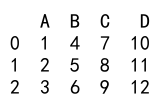
# Append multiple new columns
new_columns = {'C': [7, 8, 9], 'D': [10, 11, 12]}
for key, value in new_columns.items():
df[key] = value
print(df)
Output:
3. Using concat Function
The concat function is useful when you need to append columns from another DataFrame or Series. This function provides more flexibility compared to the previous methods.
Example 5: Concatenating a DataFrame and a Series
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Create a Series
s = pd.Series([7, 8, 9], name='C')
# Concatenate DataFrame and Series
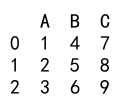
df_new = pd.concat([df, s], axis=1)
print(df_new)
Output:
Example 6: Concatenating Multiple DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'C': [7, 8, 9],
'D': [10, 11, 12]
})
# Concatenate DataFrames
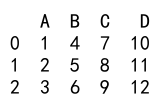
df_new = pd.concat([df1, df2], axis=1)
print(df_new)
Output:
4. Using merge Function
The merge function is typically used for joining two DataFrames based on one or more keys. However, it can also be used to append columns when the DataFrames share an index.
Example 7: Merging DataFrames on Index
import pandas as pd
# Create two Dataframes
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Merge DataFrames on index
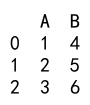
df_new = pd.merge(df1, df2, left_index=True, right_index=True, how='outer')
print(df_new)
Output:
Example 8: Using a Key to Merge DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'Key': [1, 2, 3],
'A': [4, 5, 6]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'Key': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [7, 8, 9]
})
# Merge DataFrames using a key
df_new = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Key')
print(df_new)
Output:

5. Using join Method
The join method is similar to merge but is more convenient when you want to join on the index.
Example 9: Joining DataFrames on Index
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3]
})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': [4, 5, 6]
})
# Join DataFrames on index
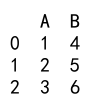
df_new = df1.join(df2)
print(df_new)
Output:
Example 10: Joining with Different Indexes
import pandas as pd
# Create two DataFrames
df1 = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 3]
}, index=[1, 2, 3])
df2 = pd.DataFrame({
'B': [4, 5, 6]
}, index=[3, 4, 5])
# Join DataFrames on index
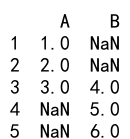
df_new = df1.join(df2, how='outer')
print(df_new)
Output:
Pandas Append Columns Conclusion
Appending columns to a DataFrame is a fundamental operation in data manipulation and analysis using Pandas. In this article, we explored various methods to append columns, including using assign, the [] operator, concat, merge, and join. Each method has its own use cases and advantages, and the choice of method depends on the specific requirements of your data manipulation task. By understanding these methods, you can efficiently manipulate data and perform complex analyses using Pandas.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe