Pandas Append Column
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that offers various functionalities for data analysis and manipulation. One common task when working with data is appending a new column to an existing DataFrame. This article will explore different methods to append columns to a DataFrame using the Pandas library. We will cover a range of techniques, from simple additions of single columns to more complex operations involving conditions and computations.
1. Adding a Single Column
The simplest way to append a column to a DataFrame is by assigning a list or array of values to a new column name. Here’s an example:
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Append a new column
df['Website'] = ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
print(df)
Output:

2. Using assign() Method
The assign() method allows you to append one or more new columns to a DataFrame. This method returns a new DataFrame, leaving the original DataFrame unchanged.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Append a new column using assign
df_new = df.assign(Website=['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'])
print(df_new)
Output:

3. Appending a Column Based on Conditions
You can append a column to a DataFrame based on certain conditions applied to the existing data. Here’s how you can do it:
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Append a new column based on condition
df['Status'] = ['Senior' if age >= 30 else 'Junior' for age in df['Age']]
print(df)
Output:
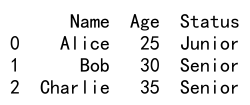
4. Using concat() to Append Multiple Columns
If you have multiple columns stored in another DataFrame or a dictionary, you can use concat() to append them to the original DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Another DataFrame
additional_data = pd.DataFrame({
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'Status': ['Junior', 'Senior', 'Senior']
})
# Concatenate columns
df = pd.concat([df, additional_data], axis=1)
print(df)
Output:

5. Appending a Column Using map()
The map() function can be used to create a new column based on the mapping of values from another column.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Employee ID': [1, 2, 3]
})
# Mapping dictionary
employee_website = {1: 'pandasdataframe.com', 2: 'pandasdataframe.com', 3: 'pandasdataframe.com'}
# Append a new column using map
df['Website'] = df['Employee ID'].map(employee_website)
print(df)
Output:

6. Using apply() to Append a Column
The apply() function allows you to apply a function along an axis of the DataFrame and append the result as a new column.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Function to categorize age
def categorize_age(age):
return 'Senior' if age >= 30 else 'Junior'
# Append a new column using apply
df['Category'] = df['Age'].apply(categorize_age)
print(df)
Output:
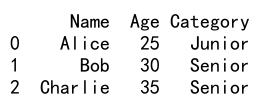
7. Appending a Column with a Default Value
Sometimes, you might want to append a column that contains a default value for all rows.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35]
})
# Append a new column with a default value
df['Website'] = 'pandasdataframe.com'
print(df)
Output:

8. Using merge() to Append Columns from Another DataFrame
If you have a separate DataFrame and want to merge it with your original DataFrame based on a key, you can use the merge() function.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Employee ID': [1, 2, 3]
})
# Another DataFrame with additional information
additional_info = pd.DataFrame({
'Employee ID': [1, 2, 3],
'Website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
})
# Merge DataFrames
df = pd.merge(df, additional_info, on='Employee ID')
print(df)
Output:

9. Appending a Computed Column
You can append a column that is computed based on other columns in the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Hours Worked': [40, 50, 45],
'Hourly Rate': [15, 20, 18]
})
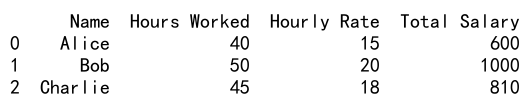
# Append a computed column for total salary
df['Total Salary'] = df['Hours Worked'] * df['Hourly Rate']
print(df)
Output:
10. Using eval() to Append a Computed Column
The eval() function in Pandas allows for efficient operations on DataFrame columns. You can use it to append a new computed column.
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Hours Worked': [40, 50, 45],
'Hourly Rate': [15, 20, 18]
})
# Append a computed column using eval
df.eval('Total Salary = Hours Worked * Hourly Rate', inplace=True)
print(df)
In conclusion, appending columns to a DataFrame in Pandas can be achieved through various methods depending on the specific requirements of your data manipulation task. Whether you’re adding a simple static column, merging data from another DataFrame, or computing values based on existing columns, Pandas provides a robust toolkit to efficiently handle these operations.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe