Pandas agg sum
Pandas is a powerful Python library for data manipulation and analysis. It provides numerous functions to perform aggregations, one of which is the sum() function. In this article, we will explore the agg() function in detail, focusing on its use with the sum() operation to perform summations over DataFrame columns.
Introduction to Pandas DataFrame
A DataFrame is a two-dimensional, size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). Before diving into examples, let’s first understand how to create a DataFrame.
Example 1: Creating a DataFrame
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eve'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'Income': [50000, 54000, 70000, 68000, 62000]
}
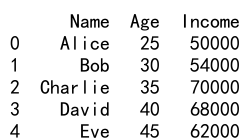
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
Output:
Basic Summation with sum()
The sum() function is used to calculate the sum of array elements over a specified axis.
Example 2: Summing a Single Column
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
total_sales = df['Sales'].sum()
print(total_sales)
Output:
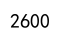
Example 3: Summing Multiple Columns
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'Expenses': [150, 200, 240, 300, 350],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
total = df[['Sales', 'Expenses']].sum()
print(total)
Output:

Using agg() for Summation
The agg() function allows more flexibility. It can apply different aggregation functions to different columns, or multiple aggregation functions to each column.
Example 4: Using agg() with sum()
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'Expenses': [150, 200, 240, 300, 350],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
result = df.agg({'Sales': 'sum', 'Expenses': 'sum'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Multiple Aggregations on a Single Column
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
result = df['Sales'].agg(['sum', 'mean'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 6: Different Aggregations for Different Columns
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'Expenses': [150, 200, 240, 300, 350],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
result = df.agg({'Sales': ['sum', 'mean'], 'Expenses': ['sum', 'max']})
print(result)
Output:

Advanced Usage of agg() and sum()
Example 7: Using Custom Functions with agg()
import pandas as pd
def increment_sum(x):
return x.sum() + 100
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
result = df['Sales'].agg(increment_sum)
print(result)
Output:
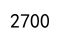
Example 8: Aggregating Over Rows
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500],
'Expenses': [150, 200, 240],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3]
})
result = df.agg('sum', axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Using agg() with Lambda Functions
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'Expenses': [150, 200, 240, 300, 350],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
result = df.agg({'Sales': lambda x: x.sum() + 500})
print(result)
Output:

Example 10: Summation with Condition
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'Sales': [300, 450, 500, 650, 700],
'Region': ['East', 'West', 'East', 'West', 'East'],
'pandasdataframe.com': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
})
sum_east = df[df['Region'] == 'East']['Sales'].sum()
print(sum_east)
Output:
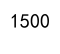
Pandas agg sum conclusion
In this article, we have explored how to use the agg() function in Pandas to perform summations and other aggregations. We’ve seen how to apply it to single columns, multiple columns, and even with custom functions. The flexibility of agg() makes it a powerful tool for data analysis, allowing for complex aggregations that are tailored to specific needs.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe