Pandas DataFrame loc Example
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python. It provides data structures and functions needed to manipulate structured data. One of the most commonly used data structure in pandas is DataFrame. DataFrame is a two-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different types.
One of the most important features of pandas DataFrame is the loc attribute. It is a label-based data selection method which means that we have to pass the name of the row or column which we want to select. This method includes the last element of the range as well, unlike iloc.
In this article, we will explore various examples of using the loc attribute with pandas DataFrame.
Example 1: Selecting a Single Row by Label
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc['Day 1'])
Output:

Example 2: Selecting Multiple Rows by Label
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc[['Day 1', 'Day 3']])
Output:

Example 3: Selecting Rows with a Boolean / Conditional Lookup
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc[df['visitors'] > 800])
Output:

Example 4: Selecting a Single Column by Label
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc[:, 'visitors'])
Output:

Example 5: Selecting Multiple Columns by Label
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc[:, ['visitors', 'signups']])
Output:

Example 6: Selecting Rows and Columns Simultaneously
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc['Day 1', 'visitors'])
Output:
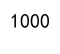
Example 7: Selecting a Range of Rows and a Range of Columns
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc['Day 1':'Day 3', 'visitors':'signups'])
Output:

Example 8: Selecting with a MultiIndex
import pandas as pd
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([(i, j) for i in ['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'] for j in ['Morning', 'Afternoon']])
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com']*6,
'visitors': [500, 500, 350, 350, 625, 625],
'signups': [25, 25, 18, 18, 24, 24]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=index)
print(df.loc[('Day 1', 'Morning')])
Output:

Example 9: Using Slice in loc
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc['Day 1':'Day 2'])
Output:

Example 10: Using loc with a Boolean Series
import pandas as pd
data = {
'website': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'visitors': [1000, 700, 1250],
'signups': [50, 36, 48]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['Day 1', 'Day 2', 'Day 3'])
print(df.loc[df['signups'] > 40])
Output:

In conclusion, the loc attribute provides a powerful and flexible way to access data in a pandas DataFrame. It allows us to select data by label, with a boolean array, or with a callable function. It also supports slicing and multi-indexing, making it a versatile tool for data selection and manipulation.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe