Pandas agg nunique
Pandas is a powerful library in Python widely used for data manipulation and analysis. In this guide, we will explore the use of the agg function combined with nunique, which is a method to count the number of unique values across different columns or rows. This functionality is particularly useful in data analysis tasks where understanding the diversity of data is required.
Introduction to Pandas agg and nunique
The agg function in Pandas is used to apply one or more operations over the specified axis. When combined with nunique, it can be used to aggregate and count unique values across multiple columns. This is especially useful in scenarios where you need to summarize data and get insights into the distribution of unique elements.
Example 1: Basic Usage of nunique
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['foo', 'bar', 'foo', 'bar', 'foo', 'bar', 'foo', 'foo'],
'B': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'three', 'two', 'two', 'one', 'three'],
'C': ['small', 'large', 'large', 'small', 'small', 'large', 'small', 'small'],
'D': [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6]
})
# Count unique values in column 'A'
unique_count = df['A'].nunique()
print(unique_count)
Output:
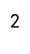
Example 2: Using agg with nunique
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'C': [1, 2, 2, 1],
'D': [1, 1, 2, 2]
})
# Apply nunique using agg
result = df.agg({'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: agg with Multiple Functions Including nunique
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'C': [2, 2, 3, 4]
})
# Apply multiple aggregation functions to column 'B'
result = df.agg({'B': ['min', 'max', 'nunique'], 'C': ['nunique']})
print(result)
Output:

Example 4: GroupBy with agg and nunique
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': ['one', 'one', 'two', 'two'],
'C': [1, 1, 2, 2],
'D': [3, 4, 3, 4]
})
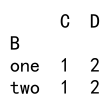
# Group by column 'B' and apply nunique on column 'C'
grouped = df.groupby('B').agg({'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(grouped)
Output:
Example 5: Using agg with Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
# Define a custom function to count unique values greater than a threshold
def count_unique_greater_than_1(series):
return series[series > 1].nunique()
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 2, 3],
'C': [1, 2, 3, 4]
})
# Apply custom function using agg
result = df.agg({'B': count_unique_greater_than_1, 'C': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Advanced Usage of agg and nunique
Example 6: Aggregating Over Multiple Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 2, 3],
'C': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'D': [5, 5, 6, 7]
})
# Apply nunique over multiple columns
result = df.agg({'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 7: Using agg with Lambda Functions
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'C': [2, 2, 3, 4]
})
# Use lambda function to count unique values
result = df.agg({'B': lambda x: x.nunique(), 'C': lambda x: x.nunique()})
print(result)
Output:

Example 8: agg with Dictionary of Lists
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'C': [5, 5, 6, 6]
})
# Apply multiple aggregation functions to each column
result = df.agg({'B': ['sum', 'nunique'], 'C': ['mean', 'nunique']})
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Combining groupby, agg, and nunique for Detailed Data Analysis
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': ['group1', 'group1', 'group2', 'group2'],
'C': [1, 1, 2, 2],
'D': [3, 4, 3, 4]
})
# Group by 'B', then aggregate with nunique and sum
grouped = df.groupby('B').agg({'C': 'nunique', 'D': ['sum', 'nunique']})
print(grouped)
Output:

Example 10: Using agg to Apply Multiple Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
# Define custom functions
def max_minus_min(x):
return x.max() - x.min()
def unique_count(x):
return x.nunique()
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [10, 20, 20, 30],
'C': [100, 200, 300, 400]
})
# Apply custom functions using agg
result = df.agg({'B': [max_minus_min, unique_count], 'C': [max_minus_min, 'nunique']})
print(result)
Output:

Example 11: Aggregating with nunique on Filtered Data
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 2, 3],
'C': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'D': [5, 5, 6, 7]
})
# Filter the DataFrame and then aggregate
filtered_df = df[df['B'] > 1]
result = filtered_df.agg({'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 12: agg and nunique Across Different Data Types
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'C': ['apple', 'banana', 'apple', 'banana'],
'D': [True, False, True, False]
})
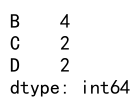
# Apply nunique to understand the diversity in each column
result = df.agg({'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:
Example 13: Dynamic Aggregation Based on Column Names
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [1, 2, 3, 4],
'C': [5, 6, 7, 8],
'D': [9, 10, 11, 12]
})
# Dynamically create a dictionary for aggregation
agg_dict = {col: 'nunique' for col in df.columns if col != 'A'}
result = df.agg(agg_dict)
print(result)
Output:

Example 14: Aggregating with nunique and Handling NaN Values
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a DataFrame with NaN values
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', np.nan, 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [np.nan, 2, 2, 3],
'C': [1, np.nan, 3, 4],
'D': [5, 5, 6, 7]
})
# Count unique values ignoring NaN
result = df.agg({'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique', 'D': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 15: Using agg with nunique in Time Series Data
import pandas as pd
# Create a time series DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.date_range(start='2023-01-01', periods=4, freq='D'),
'B': [1, 1, 2, 2],
'C': [3, 4, 3, 4]
})
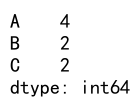
# Apply nunique to count unique dates and values
result = df.agg({'A': 'nunique', 'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:
Example 16: Combining agg with nunique for Multi-Index DataFrames
import pandas as pd
# Create a Multi-Index DataFrame
arrays = [['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'], ['one', 'one', 'two', 'two']]
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=('Upper', 'Lower'))
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 4, 5, 5]}, index=index)
# Apply nunique on a multi-index DataFrame
result = df.agg({'A': 'nunique', 'B': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 17: agg with nunique for Categorical Data
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with categorical data
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.Categorical(['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']),
'B': pd.Categorical(['small', 'large', 'large', 'small']),
'C': [1, 2, 2, 1]
})
# Apply nunique to categorical columns
result = df.agg({'A': 'nunique', 'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:
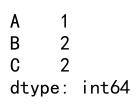
Example 18: Using agg and nunique with a Custom Index
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with a custom index
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1, 2, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 4, 5, 5]
}, index=['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'])
# Apply nunique and specify the index
result = df.agg({'A': 'nunique', 'B': 'nunique'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 19: agg and nunique with Sorting
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [4, 1, 3, 2],
'C': [2, 1, 3, 4]
})
# Apply nunique and sort results
result = df.agg({'B': 'nunique', 'C': 'nunique'}).sort_values(ascending=False)
print(result)
Output:

Example 20: Detailed Aggregation with agg, nunique, and Descriptive Statistics
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com'],
'B': [10, 20, 20, 30],
'C': [100, 200, 300, 400]
})
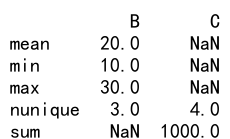
# Apply multiple aggregation functions including nunique
result = df.agg({'B': ['mean', 'min', 'max', 'nunique'], 'C': ['sum', 'nunique']})
print(result)
Output:
Pandas agg nunique conclusion
This comprehensive guide has demonstrated various ways to use the agg function along with nunique in Pandas to perform complex data aggregations. These examples illustrate how to handle different data types, deal with NaN values, work with time series, and much more. By mastering these techniques, you can effectively analyze and summarize your data, gaining deeper insights into its unique characteristics. Whether you are dealing with simple or complex datasets, the flexibility of Pandas ensures that you have the tools necessary to extract meaningful information efficiently.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe