Pandas astype Float
Pandas is a powerful and flexible open-source data analysis and manipulation library for Python. One of the common tasks in data manipulation is converting data types. The astype method in Pandas is used to cast a pandas object to a specified data type. In this article, we will delve into the details of using the astype method to convert data types to float in Pandas DataFrames.
1. Introduction to astype
The astype method in Pandas is used to cast a pandas object to a specified data type. This method is very flexible and can be used to convert a single column or multiple columns in a DataFrame. The syntax for the astype method is as follows:
DataFrame.astype(dtype, copy=True, errors='raise')
dtype: Data type to cast to.copy: Whether to return a copy of the DataFrame (default is True).errors: Control raising of exceptions on invalid data for provided dtype. Options are ‘raise’, ‘ignore’.
2. Basic Usage of astype to Convert to Float
Let’s start with a basic example of converting a single column in a DataFrame to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3'],
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, we create a DataFrame with two columns, ‘A’ and ‘B’, both containing string representations of numbers. We then use the astype method to convert column ‘A’ to float.
3. Converting Specific Columns to Float
You can also convert multiple specific columns to float by passing a dictionary to the astype method.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3'],
'B': ['4', '5', '6'],
'C': ['7', '8', '9']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to float
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'B': float})
print(df)
Output:
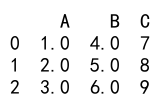
In this example, we convert columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ to float by passing a dictionary to the astype method.
4. Handling Missing Values During Conversion
When converting columns with missing values (NaNs) to float, the astype method handles them gracefully.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a sample DataFrame with missing values
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', np.nan],
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

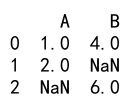
In this example, column ‘A’ contains a missing value (NaN). The astype method converts the column to float and retains the NaN value.
5. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Mixed Types
If your DataFrame contains columns with mixed data types, you can still use the astype method to convert specific columns to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with mixed types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3'],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': ['7', '8', '9']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'C' to float
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'C': float})
print(df)
Output:

In this example, columns ‘A’ and ‘C’ are converted to float, while column ‘B’ remains as an integer.
6. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with String Representations of Numbers
If your DataFrame contains string representations of numbers, you can use the astype method to convert them to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with string representations of numbers
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1.1', '2.2', '3.3'],
'B': ['4.4', '5.5', '6.6']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to float
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'B': float})
print(df)
Output:

In this example, columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ contain string representations of floating-point numbers. The astype method converts them to float.
7. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Non-Numeric Strings
If your DataFrame contains non-numeric strings, attempting to convert them to float will raise an error. You can handle this by using the errors parameter.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with non-numeric strings
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'three'],
'B': ['4', 'five', '6']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to float, ignoring errors
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'B': float}, errors='ignore')
print(df)
Output:
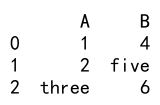
In this example, columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ contain non-numeric strings. The astype method ignores the errors and leaves the non-numeric strings unchanged.
8. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with DateTime Columns
You can also convert DateTime columns to float, where the float represents the number of seconds since the epoch.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with DateTime column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.to_datetime(['2023-01-01', '2023-01-02', '2023-01-03']),
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert DateTime column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype('int64') / 1e9
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ contains DateTime values. We convert them to float by first converting to int64 (nanoseconds since the epoch) and then dividing by 1e9 to get seconds.
9. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Boolean Columns
Boolean columns can also be converted to float, where True becomes 1.0 and False becomes 0.0.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with Boolean column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [True, False, True],
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert Boolean column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ contains Boolean values. The astype method converts them to float, with True becoming 1.0 and False becoming 0.0.
10. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Categorical Columns
Categorical columns can be converted to float, where the categories are represented by their codes.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with Categorical column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.Categorical(['low', 'medium', 'high']),
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert Categorical column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].cat.codes.astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ contains categorical values. We first convert the categories to their codes and then use the astype method to convert them to float.
11. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Object Columns
Object columns can be converted to float if they contain numeric values.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with Object column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3'],
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert Object column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ is an object column containing string representations of numbers. The astype method converts it to float.
12. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Complex Numbers
Complex number columns can be converted to float, but this will only keep the real part of the complex numbers.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with Complex number column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': [1+2j, 3+4j, 5+6j],
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert Complex number column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].apply(lambda x: x.real).astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ contains complex numbers. We use the apply method to extract the real part and then convert it to float.
13. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Custom Functions
You can use custom functions to handle more complex conversions to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'three'],
'B': ['4', 'five', '6']
})
# Define a custom function to convert to float
def custom_convert(x):
try:
return float(x)
except ValueError:
return None
# Apply the custom function to columns 'A' and 'B'
df['A'] = df['A'].apply(custom_convert)
df['B'] = df['B'].apply(custom_convert)
print(df)
Output:
In this example, we define a custom function custom_convert that attempts to convert a value to float and returns None if it fails. We then apply this function to columns ‘A’ and ‘B’.
14. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with MultiIndex
You can also convert data types in a DataFrame with a MultiIndex.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with MultiIndex
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('A', 1), ('A', 2), ('B', 1), ('B', 2)], names=['first', 'second'])
df = pd.DataFrame({
'C': ['1', '2', '3', '4'],
'D': ['5', '6', '7', '8']
}, index=index)
# Convert column 'C' to float
df['C'] = df['C'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, we create a DataFrame with a MultiIndex and convert column ‘C’ to float.
15. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with TimeDelta Columns
TimeDelta columns can be converted to float, where the float represents the number of seconds.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with TimeDelta column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.to_timedelta(['1 days', '2 days', '3 days']),
'B': ['4', '5', '6']
})
# Convert TimeDelta column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].dt.total_seconds().astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ contains TimeDelta values. We convert them to float by extracting the total number of seconds.
16. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Sparse Columns
Sparse columns can also be converted to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with Sparse column
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': pd.arrays.SparseArray([1, 0, 0, 2]),
'B': ['4', '5', '6', '7']
})
# Convert Sparse column 'A' to float
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float)
print(df)
Output:

In this example, column ‘A’ is a sparse column. The astype method converts it to float.
17. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Mixed Data Types
If your DataFrame contains mixed data types, you can still use the astype method to convert specific columns to float.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', '3'],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': ['7', '8', '9']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'C' to float
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'C': float})
print(df)
Output:

In this example, columns ‘A’ and ‘C’ are converted to float, while column ‘B’ remains as an integer.
18. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Large Datasets
When working with large datasets, converting data types to float can be memory-intensive. You can use the copy=False parameter to avoid creating a copy of the DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
# Create a large sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1'] * 1000000,
'B': ['2'] * 1000000
})
# Convert column 'A' to float without creating a copy
df['A'] = df['A'].astype(float, copy=False)
print(df)
Output:
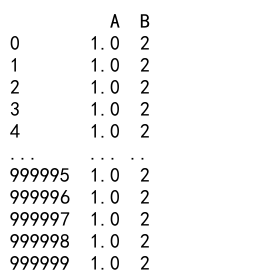
In this example, we create a large DataFrame and convert column ‘A’ to float without creating a copy.
19. Converting Data Types in a DataFrame with Performance Considerations
When performance is a concern, you can use the errors='ignore' parameter to skip over any conversion errors.
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame with mixed data types
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': ['1', '2', 'three'],
'B': ['4', 'five', '6']
})
# Convert columns 'A' and 'B' to float, ignoring errors
df = df.astype({'A': float, 'B': float}, errors='ignore')
print(df)
Output:
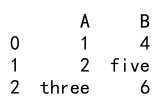
In this example, columns ‘A’ and ‘B’ contain non-numeric strings. The astype method ignores the errors and leaves the non-numeric strings unchanged.
20. Pandas astype Float Conclusion
In this article, we have explored various ways to use the astype method in Pandas to convert data types to float. We have covered basic usage, handling missing values, converting specific columns, and dealing with different data types such as DateTime, Boolean, Categorical, Object, Complex numbers, and more. By understanding these techniques, you can effectively manage data type conversions in your Pandas DataFrames.
Remember, the astype method is a powerful tool in your data manipulation toolkit, and mastering it will help you handle a wide range of data conversion scenarios in Pandas.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe