Pandas Agg Function
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python, widely used in data analysis and data science. One of its versatile features is the agg function, which allows for applying different aggregation operations to a DataFrame or a Series. This article will explore the agg function in-depth, providing a comprehensive guide on how to use it effectively in various scenarios. We will include numerous examples to demonstrate its flexibility and utility.
Introduction to Pandas Agg Function
The agg function, short for “aggregate,” is used to apply one or more operations over the specified axis. It is particularly useful when you need to perform multiple aggregations on a dataset at once or when you need to apply different functions to different columns of a DataFrame.
Pandas Agg Function Basic Usage
The basic syntax of the agg function is as follows:
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using agg to apply a single function
result = df.agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Applying Multiple Functions
You can apply multiple functions at once using a list:
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Applying multiple functions to all columns
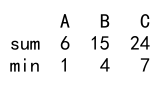
result = df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
print(result)
Output:
Detailed Examples of Pandas Agg Function
Let’s dive into more detailed examples to showcase the power and flexibility of the agg function.
Example 1: Single Function to All Columns
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Applying sum to all columns
result = df.agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Example 2: Multiple Functions to All Columns
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Applying multiple aggregation functions
result = df.agg(['sum', 'mean', 'std'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Different Functions to Different Columns
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Applying different functions to different columns
result = df.agg({
'pandasdataframe.com_A': 'sum',
'pandasdataframe.com_B': 'mean',
'pandasdataframe.com_C': ['min', 'max']
})
print(result)
Output:

Example 4: Using Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Defining a custom function
def range_func(x):
return x.max() - x.min()
# Applying custom function
result = df.agg(range_func)
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Aggregation on Series
import pandas as pd
data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
series = pd.Series(data, name='pandasdataframe.com_Series')
# Applying aggregation on a Series
result = series.agg(['sum', 'mean'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 6: Aggregation with Lambda Functions
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using lambda functions for aggregation
result = df.agg({
'pandasdataframe.com_A': lambda x: x ** 2,
'pandasdataframe.com_B': lambda x: x + 10
})
print(result)
Example 7: Aggregation on DataFrame with Missing Values
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, None, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [None, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, None]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Handling missing values during aggregation
result = df.agg('sum', skipna=True)
print(result)
Output:

Example 8: Aggregation Using Numpy Functions
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using numpy functions for aggregation
result = df.agg(np.sum)
print(result)
Example 9: Chain Aggregations
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Chaining aggregations
result = df.agg('sum').agg('mean')
print(result)
Output:
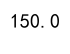
Example 10: Aggregation on Filtered Data
import pandas as pd
data = {
'pandasdataframe.com_A': [10, 20, 30],
'pandasdataframe.com_B': [40, 50, 60],
'pandasdataframe.com_C': [70, 80, 90]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Aggregation on filtered data
filtered_result = df[df['pandasdataframe.com_A'] > 15].agg('sum')
print(filtered_result)
Output:

Pandas Agg Function Conclusion
The agg function in Pandas is a powerful tool for data aggregation, offering flexibility to apply multiple and varied functions across different columns and data structures. By understanding and utilizing this function, you can perform complex data analysis tasks efficiently. The examples provided in this article should help you get started with using the agg function in your data analysis projects.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe