Pandas DataFrame: Using .loc with Two Conditions
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that provides data structures and functions for effectively handling and analyzing large datasets. One of the most versatile and commonly used data structures in Pandas is the DataFrame. A DataFrame is a two-dimensional, size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns).
One of the key features of DataFrame is the ability to perform indexing and subsetting of data. The .loc attribute is one of the primary tools for performing these operations. It allows for label-based indexing, which means you can subset the data based on the labels of the rows and columns. In this article, we will explore how to use the .loc method specifically with two conditions, which is a common scenario in data analysis.
Understanding .loc Method
The .loc method is used for accessing a group of rows and columns by labels or a boolean array. .loc is primarily label based, but may also be used with a boolean array. The key syntax to remember is:
dataframe.loc[row_labels, column_labels]
Where row_labels and column_labels can be labels, lists of labels, a slice object with labels, or a boolean array.
Using .loc with Two Conditions
When you need to filter data based on multiple conditions, you can use logical operators like & (and), | (or), and ~ (not) within the .loc method. It’s important to wrap each condition in parentheses due to Python’s operator precedence rules.
Example 1: Basic Usage of .loc with Two Conditions
import pandas as pd
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with two conditions
result = df.loc[(df['Age'] > 30) & (df['City'] == 'Chicago'), :]
print(result)
Output:
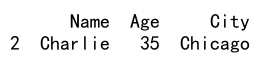
Example 2: Selecting Specific Columns with Two Conditions
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Select specific columns with conditions
result = df.loc[(df['Age'] > 30) & (df['City'] == 'Houston'), ['Name', 'Email']]
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Using OR Condition
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using OR condition
result = df.loc[(df['Age'] < 35) | (df['City'] == 'Phoenix'), :]
print(result)
Output:

Example 4: Combining Conditions with NOT
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using NOT condition
result = df.loc[(df['Age'] > 30) & ~(df['City'] == 'Chicago'), :]
print(result)
Output:
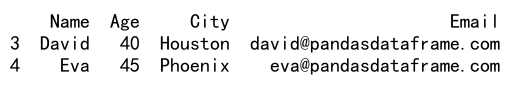
Example 5: Filtering with String Methods
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Filtering with string methods
result = df.loc[df['Email'].str.contains('pandasdataframe.com') & (df['Age'] > 30), :]
print(result)
Output:
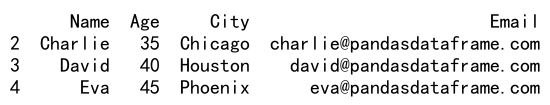
Example 6: Using .loc with Date Conditions
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame with dates
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Join_Date': pd.to_datetime(['2021-01-01', '2021-02-15', '2021-03-01', '2021-04-01', '2021-05-01']),
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with date conditions
result = df.loc[(df['Join_Date'] > '2021-01-31') & (df['City'] == 'Houston'), :]
print(result)
Output:
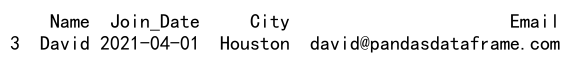
Example 7: Using .loc with Categorical Data
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame with categorical data
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Department': pd.Categorical(['HR', 'Marketing', 'IT', 'Finance', 'HR']),
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with categorical data
result = df.loc[(df['Department'] == 'HR') & (df['City'] == 'Phoenix'), :]
print(result)
Output:

Example 8: Using .loc with Numerical Ranges
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Salary': [50000, 60000, 70000, 80000, 90000],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with numerical ranges
result = df.loc[(df['Salary'] >= 60000) & (df['Salary'] <= 80000), :]
print(result)
Output:
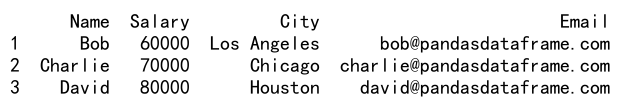
Example 9: Combining Text and Numerical Filters
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Combining text and numerical filters
result = df.loc[(df['Name'].str.startswith('A')) & (df['Age'] > 20), :]
print(result)
Output:
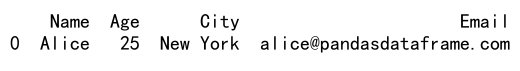
Example 10: Using .loc with Isin Method
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with isin method
cities = ['Chicago', 'Houston']
result = df.loc[df['City'].isin(cities) & (df['Age'] > 30), :]
print(result)
Output:
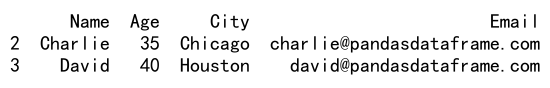
Example 11: Filtering Based on Index Labels
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame with specific index
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index=['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
# Filtering based on index labels
result = df.loc[(df.index == 'C') | (df.index == 'D'), :]
print(result)
Output:
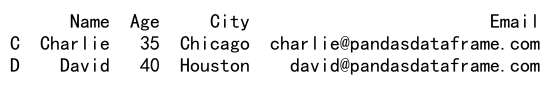
Example 12: Using .loc with Lambda Functions
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using .loc with lambda functions
result = df.loc[lambda x: (x['Age'] > 30) & (x['City'].str.contains('New')), :]
print(result)
Output:

Example 13: Complex Conditions with Multiple Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]'],
'Status': ['Active', 'Inactive', 'Active', 'Active', 'Inactive']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Complex conditions with multiple columns
result = df.loc[(df['Status'] == 'Active') & (df['Age'] > 30) & (df['City'].str.contains('New')), :]
print(result)
Output:
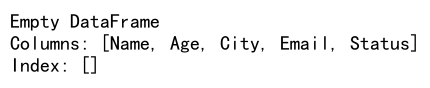
Example 14: Resetting Index Before Using .loc
import pandas as pd
# Create DataFrame
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie', 'David', 'Eva'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40, 45],
'City': ['New York', 'Los Angeles', 'Chicago', 'Houston', 'Phoenix'],
'Email': ['[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]', '[email protected]']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Resetting index
df.reset_index(drop=True, inplace=True)
# Using .loc after resetting index
result = df.loc[(df['Age'] > 30) & (df['City'] == 'Houston'), :]
print(result)
Output:
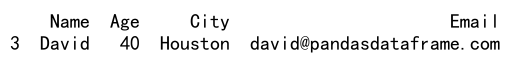
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe