Pandas DataFrame loc with MultiIndex
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python that provides data structures and functions for effectively handling and analyzing large datasets. One of the key features of Pandas is the DataFrame, which is a two-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different types. In this article, we will explore how to use the loc method in conjunction with a MultiIndex in a Pandas DataFrame.
Introduction to MultiIndex
A MultiIndex, or hierarchical index, allows you to have multiple levels of indices on a single axis. It is a concept in Pandas that provides a way to work with higher dimensional data using a lower dimensional structure. MultiIndex can be thought of as an array of tuples where each tuple is unique.
Creating a MultiIndex DataFrame
Before diving into the loc method, let’s first understand how to create a MultiIndex DataFrame. Here’s an example:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
print(df)
Output:

Using loc with MultiIndex
The loc method is used for label-based indexing, which means that you can index the data using explicit labels instead of integer locations. When dealing with MultiIndex, loc can be used to access a subset of the DataFrame by specifying the labels.
Accessing Single Elements
Here’s how you can access a single element using loc in a MultiIndex DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Access data at a specific index
data = df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'A')]
print(data)
Output:

Accessing Subsets
You can also access a subset of the DataFrame by specifying a range of labels:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Access data at a specific index
data = df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'A')]
# Access a subset of the DataFrame
subset = df.loc['pandasdataframe.com']
print(subset)
Output:

Using Slices
You can use slices to select data over a range of labels:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Slice the DataFrame
sliced_data = df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'):('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')]
print(sliced_data)
Output:

Conditional Selection
loc can also be combined with boolean arrays to make conditional selections:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Conditional selection
condition = df['Data'] > 1
selected_data = df.loc[condition]
print(selected_data)
Output:

Using loc with Cross-section
The xs method can be used in conjunction with loc to get cross-sections of the data:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Get cross-section using xs
cross_section = df.xs('pandasdataframe.com', level='Website')
print(cross_section)
Output:

Setting Values
You can also use loc to set values in the DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Set values using loc
df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), 'Data'] = 100
print(df)
Output:

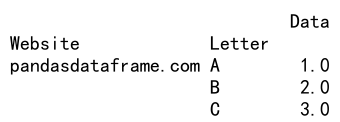
Adding a Row
Adding a row in a MultiIndex DataFrame using loc can be done as follows:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Add a row to the DataFrame
df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'C'), 'Data'] = 3
print(df)
Output:
Deleting a Row
Similarly, deleting a row can be achieved using drop:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Delete a row from the DataFrame
df = df.drop(('pandasdataframe.com', 'B'))
print(df)
Output:

Multi-Level Indexing
When dealing with multiple levels, you can specify the levels you want to access:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Multi-level indexing
multi_level_data = df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', slice(None)), :]
print(multi_level_data)
Output:

Using loc with Sorting
It’s often useful to sort the MultiIndex before using loc for better performance:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Sort the index
df = df.sort_index()
sorted_data = df.loc[('pandasdataframe.com', 'A')]
print(sorted_data)
Output:

Resetting the Index
After extensive indexing, you might want to reset the index of the DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Reset the index
reset_df = df.reset_index()
print(reset_df)
Output:

Advanced Conditional Selection
For more complex conditions, you can use logical operators:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Advanced conditional selection
advanced_selected_data = df.loc[(df['Data'] > 1) & (df.index.get_level_values('Letter') == 'A')]
print(advanced_selected_data)
Output:

Updating Multiple Rows
To update multiple rows based on a condition:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Update multiple rows
df.loc[df['Data'] > 1, 'Data'] = 10
print(df)
Output:

Using loc with Functions
You can also use functions to manipulate the data accessed by loc:
import pandas as pd
# Create a MultiIndex from tuples
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_tuples([('pandasdataframe.com', 'A'), ('pandasdataframe.com', 'B')], names=['Website', 'Letter'])
# Create a DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [1, 2]}, index=index)
# Using loc with a function
def multiply_data(x):
return x * 10
df['Data'] = df.loc[:, 'Data'].apply(multiply_data)
print(df)
Output:

Pandas DataFrame loc with MultiIndex Conclusion
Using loc with a MultiIndex in Pandas is a powerful way to access and manipulate data in a DataFrame. By understanding how to effectively use loc, you can perform a wide range of data manipulation tasks more efficiently. Whether you’re accessing single elements, subsets, or using conditions, loc provides a robust solution for indexing and selecting data in a MultiIndex DataFrame.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe