Comprehensive Guide to Using agg and count in Pandas
Pandas is a powerful Python library for data manipulation and analysis, providing data structures and operations for manipulating numerical tables and time series. This article focuses on two essential methods: agg and count. We will explore how to use these methods to summarize and analyze data efficiently.
Introduction to Pandas agg Method
The agg method in Pandas is used to apply one or more operations over the specified axis. It is particularly useful for running multiple aggregations on a DataFrame or a Series simultaneously.
Example 1: Basic Usage of agg with a Single Function
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Use agg to apply a single function
result = df.agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Example 2: Using agg with Multiple Functions
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'A': [10, 20, 30],
'B': [40, 50, 60],
'C': [70, 80, 90],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Apply multiple aggregation functions
result = df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Applying Different Functions to Different Columns
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'A': [100, 200, 300],
'B': [400, 500, 600],
'C': [700, 800, 900],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Apply different functions to different columns
result = df.agg({'A': 'sum', 'B': 'min', 'C': 'max'})
print(result)
Output:

Introduction to Pandas count Method
The count method in Pandas is used to count non-NA cells for each column or row.
Example 4: Counting Non-NA Cells in a DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame with NA values
data = {
'A': [1, None, 3],
'B': [4, 5, None],
'C': [7, 8, 9],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', None, 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Count non-NA cells in the DataFrame
result = df.count()
print(result)
Output:

Example 5: Counting Non-NA Cells Across a Specific Axis
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [None, None, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Count non-NA cells across rows
result = df.count(axis=1)
print(result)
Output:

Advanced Usage of agg in GroupBy Operations
GroupBy operations are significantly enhanced by the agg method, allowing for complex aggregations.
Example 6: GroupBy with agg
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Group': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'],
'Value': [10, 15, 10, 20],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Group by 'Group' column and sum 'Value'
result = df.groupby('Group').agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Example 7: Multiple Aggregations after GroupBy
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Group': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'],
'Value': [5, 10, 15, 20],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Apply multiple aggregations
result = df.groupby('Group').agg(['sum', 'mean'])
print(result)
Example 8: Different Aggregations for Different Columns in GroupBy
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Group': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'],
'Value1': [5, 10, 15, 20],
'Value2': [50, 100, 150, 200],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Apply different aggregations to different columns
result = df.groupby('Group').agg({'Value1': 'sum', 'Value2': 'mean'})
print(result)
Output:
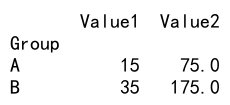
Combining agg and count for Comprehensive Data Analysis
Combining these methods can provide deeper insights into the data.
Example 9: Using count with GroupBy
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'Group': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B'],
'Value': [None, 10, 15, None],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Count non-NA 'Value' per group
result = df.groupby('Group')['Value'].count()
print(result)
Output:

Example 10: Using agg with Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
# Create a DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, 3],
'B': [4, 5, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9],
'D': ['pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com', 'pandasdataframe.com']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Define a custom aggregation function
def my_custom_function(x):
return x.max() - x.min()
# Apply custom function using agg
result = df.agg(my_custom_function)
print(result)
This guide has provided a detailed overview of using agg and count in Pandas, complete with practical examples. These tools are essential for effective data analysis and can be adapted to various data scenarios.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe