Pandas DataFrame loc vs iloc
Pandas is a powerful data manipulation library in Python. It provides two main data structures: Series and DataFrame. In this article, we will focus on the DataFrame and two of its important indexing functions: loc and iloc.
Introduction to DataFrame
A DataFrame is a two-dimensional labeled data structure with columns of potentially different types. It is similar to a spreadsheet or SQL table, or a dictionary of Series objects. It is generally the most commonly used pandas object.
Here is an example of how to create a DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
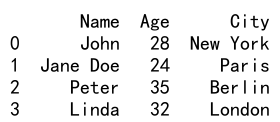
data = {
'Name': ['John', 'Anna', 'Peter', 'Linda'],
'Age': [28, 24, 35, 32],
'City': ['New York', 'Paris', 'Berlin', 'London']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
Output:

Introduction to loc and iloc
loc and iloc are two indexing functions used to select data from a DataFrame.
loc is label-based, which means that you have to specify the name of the rows and columns that you need to filter out. On the other hand, iloc is integer index-based. So here, you have to specify rows and columns by their integer index.
Here is an example of how to use loc and iloc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['John', 'Anna', 'Peter', 'Linda'],
'Age': [28, 24, 35, 32],
'City': ['New York', 'Paris', 'Berlin', 'London']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using loc
print(df.loc[1, 'Name'])
# Using iloc
print(df.iloc[1, 0])
Output:
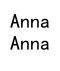
Differences between loc and iloc
The main differences between loc and iloc are:
locis label-based data selection method which means that we have to pass the name of the row or column which we want to select. This method includes the last element of the range. Whileilocis integer index-based selection method which means that we have to pass integer index in the method and it excludes the last element of the range.-
loccan accept the boolean data, it will return a DataFrame of bool values and it can be useful with theanymethod to check if any value is True in the DataFrame. Whileilocdoesn’t work with the boolean data.
Here is an example of how to use loc and iloc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['John', 'Anna', 'Peter', 'Linda'],
'Age': [28, 24, 35, 32],
'City': ['New York', 'Paris', 'Berlin', 'London']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
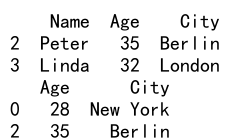
# Using loc
print(df.loc[df['Age'] > 30])
# Using iloc
print(df.iloc[[0, 2], [1, 2]])
Output:
When to use loc and iloc
You should use loc when you want to access a group of rows and columns by label(s) or a boolean array. loc is primarily label based, but may also be used with a boolean array.
You should use iloc when you want to access a group of rows and columns by integer position(s). iloc is primarily integer position based, but may also be used with a boolean array.
Here is an example of how to use loc and iloc:
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['John', 'Anna', 'Peter', 'Linda'],
'Age': [28, 24, 35, 32],
'City': ['New York', 'Paris', 'Berlin', 'London']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using loc
print(df.loc[df['City'].str.contains('pandasdataframe.com')])
# Using iloc
print(df.iloc[0:2, 0:2])
Output:
Advanced usage of loc and iloc
You can also use loc and iloc to modify data in a DataFrame.
Here is an example of how to use loc and iloc to modify data:
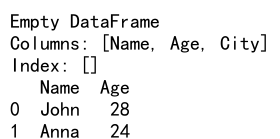
import pandas as pd
data = {
'Name': ['John', 'Anna', 'Peter', 'Linda'],
'Age': [28, 24, 35, 32],
'City': ['New York', 'Paris', 'Berlin', 'London']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using loc
df.loc[1, 'Name'] = 'John Doe'
# Using iloc
df.iloc[1, 0] = 'Jane Doe'
print(df)
Output:
Pandas DataFrame loc vs iloc Conclusion
In this article, we have discussed the differences between loc and iloc in pandas DataFrame. Both loc and iloc are very useful functions when it comes to selecting data from a DataFrame. The main difference between them is that loc is label-based while iloc is integer index-based. You should use loc when you want to access data by label or by a boolean array, and use iloc when you want to access data by integer position.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe