Pandas agg List
Pandas is a powerful Python library used for data manipulation and analysis. One of its core functionalities is the ability to perform aggregation operations on dataframes. The agg function is particularly versatile, allowing users to apply a variety of aggregation methods to a series or dataframe. This article will explore the agg function in-depth, providing a comprehensive guide on its usage with multiple examples.
Introduction to Pandas agg Function
The agg function in Pandas is used to apply one or more operations over the specified axis of a DataFrame or a Series. It is highly flexible, enabling the application of built-in aggregation functions, custom functions, or a combination of both. This function is particularly useful in summarizing data, performing statistical analysis, and data transformation.
Basic Usage of agg
Before diving into examples, let’s first understand the basic usage of the agg function. Here is a simple example:
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Create a sample DataFrame
data = {
'A': [1, 2, np.nan],
'B': [4, np.nan, 6],
'C': [7, 8, 9]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Using agg to find the sum of each column
result = df.agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, agg is used to calculate the sum of each column in the DataFrame.
Detailed Examples of Using agg
Now, let’s explore various ways to use the agg function with detailed examples. Each example will be standalone and can be run independently.
Example 1: Single Function Aggregation
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
# Aggregate using a single function
result = df.agg('mean')
print(result)
Output:

Example 2: Multiple Function Aggregation on DataFrame
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
# Aggregate using multiple functions
result = df.agg(['sum', 'min'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 3: Different Functions for Each Column
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
# Aggregate using different functions for each column
result = df.agg({'A': 'sum', 'B': 'max', 'C': 'mean'})
print(result)
Output:

Example 4: Using Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
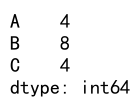
# Define a custom function
def my_custom_func(x):
return x.max() - x.min()
# Aggregate using a custom function
result = df.agg(my_custom_func)
print(result)
Output:
Example 5: Multiple Aggregations on Series
import pandas as pd
# Sample Series
s = pd.Series(range(10, 20))
# Multiple aggregations
result = s.agg(['sum', 'mean'])
print(result)
Output:

Example 6: Aggregating with Named Aggregations
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
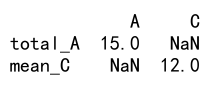
# Named aggregations
result = df.agg(total_A=('A', 'sum'), mean_C=('C', 'mean'))
print(result)
Output:
Example 7: Aggregating with Filters
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
# Aggregate with a filter
result = df[df['A'] > 2].agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Example 8: Using agg in GroupBy Operations
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'key': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'A'],
'data': range(5),
'values': [100, 200, 300, 400, 500]
})
# Group by 'key' and aggregate
result = df.groupby('key').agg('sum')
print(result)
Output:

Example 9: Complex Aggregations
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({
'A': range(1, 6),
'B': range(10, 0, -2),
'C': range(10, 15)
})
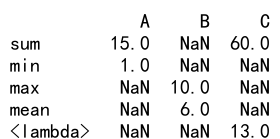
# Complex aggregations
result = df.agg({
'A': ['sum', 'min'],
'B': ['max', 'mean'],
'C': ['sum', lambda x: x.mean() + 1]
})
print(result)
Output:
Pandas agg List Conclusion
The agg function in Pandas is a powerful tool for data aggregation, offering flexibility to apply multiple and complex aggregations across different axes of a DataFrame or Series. By understanding and utilizing this function effectively, you can perform a wide range of data summarization and transformation tasks, which are essential for data analysis and decision-making processes.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe