Pandas astype datetime
Pandas is a powerful and flexible Python library for data analysis and manipulation. One of the most common tasks when working with data is handling date and time information. This often requires converting columns of a DataFrame to datetime objects. Pandas provides robust methods to handle such conversions, with the astype method being one of the most straightforward.
In this article, we will explore the astype method in pandas and how it can be used to convert columns to datetime objects.
1. Introduction to Pandas astype Method
The astype method in pandas is used to cast a pandas object to a specified dtype. This method is incredibly flexible and can be used for various data types, including integers, floats, strings, and datetime.
Example Code:
import pandas as pd
# Creating a sample DataFrame
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08', '2024-08-09', '2024-09-10'],
'numbers': [1, 2, 3]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting the 'date_strings' column to datetime
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
print(df)
Output:

In the example above, we have a DataFrame with a column of date strings. We use the astype method to convert these strings into datetime objects.
2. Converting Strings to Datetime
When working with date and time data, it’s common to start with date and time in string format. Converting these strings to datetime objects allows for more efficient and accurate operations.
Example Code:
import pandas as pd
# Sample data
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08 10:00:00', '2024-08-09 15:30:00', '2024-09-10 20:45:00']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
print(df)
Output:

This example demonstrates converting strings with both date and time components into datetime objects.
3. Handling Different Date Formats
Date strings can come in various formats, and pandas can handle many of these formats seamlessly. However, there are times when you need to specify the format explicitly.
Example Code:
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with different date formats
data = {
'date_strings': ['08-07-2024', '09-08-2024', '10-09-2024']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting with specified format
df['date_strings'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date_strings'], format='%d-%m-%Y')
print(df)
Output:

In this example, we use the pd.to_datetime function with the format parameter to handle date strings in the dd-mm-yyyy format.
4. Working with Time Components
Sometimes, the time component of the date strings is essential for the analysis. Pandas can handle and manipulate these components effectively.
Example Code:
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with time components
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08 10:00:00', '2024-08-09 15:30:00', '2024-09-10 20:45:00']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
# Extracting time components
df['hour'] = df['date_strings'].dt.hour
df['minute'] = df['date_strings'].dt.minute
df['second'] = df['date_strings'].dt.second
print(df)
Output:

Here, we convert strings to datetime and then extract the hour, minute, and second components.
5. Dealing with Missing or Invalid Dates
Real-world data often includes missing or invalid dates. Pandas provides robust methods to handle such scenarios gracefully.
Example Code:
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with missing dates
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08', None, '2024-09-10']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime, handling missing values
df['date_strings'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date_strings'], errors='coerce')
print(df)
Output:
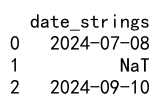
In this example, the errors='coerce' parameter converts invalid parsing to NaT (Not a Time), which pandas handles efficiently.
6. Practical Examples
Let’s explore some practical examples where datetime conversions are essential.
Example 1: Calculating Duration
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with start and end times
data = {
'start_time': ['2024-07-08 10:00:00', '2024-08-09 15:30:00', '2024-09-10 20:45:00'],
'end_time': ['2024-07-08 11:00:00', '2024-08-09 16:00:00', '2024-09-10 21:15:00']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime
df['start_time'] = df['start_time'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
df['end_time'] = df['end_time'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
# Calculating duration
df['duration'] = df['end_time'] - df['start_time']
print(df)
Output:

Example 2: Filtering Data by Date
import pandas as pd
# Sample data
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08', '2024-08-09', '2024-09-10']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
# Filtering data
filtered_df = df[df['date_strings'] > '2024-08-01']
print(filtered_df)
Output:

Example 3: Time Series Analysis
import pandas as pd
# Sample data
data = {
'date_strings': pd.date_range(start='2024-01-01', periods=100, freq='D'),
'values': range(100)
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Setting the date column as index
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].astype('datetime64[ns]')
df.set_index('date_strings', inplace=True)
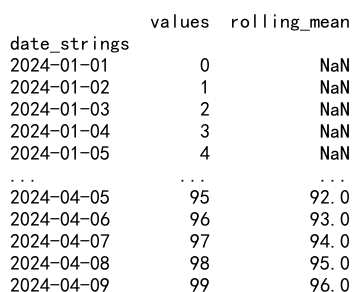
# Performing rolling mean
df['rolling_mean'] = df['values'].rolling(window=7).mean()
print(df)
Output:
8. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
Issue 1: Incorrect Date Format
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with incorrect format
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024/07/08', '2024/08/09', '2024/09/10']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime with specified format
try:
df['date_strings'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date_strings'], format='%Y-%m-%d')
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
print(df)
Output:

Issue 2: Handling Mixed Date Formats
import pandas as pd
# Sample data with mixed formats
data = {
'date_strings': ['2024-07-08', '08/09/2024', 'September 10, 2024']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Converting to datetime
df['date_strings'] = pd.to_datetime(df['date_strings'], errors='coerce')
print(df)
Output:
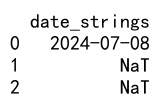
9. Advanced Usage
Custom Date Parser
import pandas as pd
from dateutil import parser
# Sample data with custom format
data = {
'date_strings': ['08-July-2024', '09-August-2024', '10-September-2024']
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Custom date parser
df['date_strings'] = df['date_strings'].apply(lambda x: parser.parse(x))
print(df)
Output:

10. Pandas astype datetime Summary and Best Practices
Converting date and time data to datetime objects is crucial for efficient data analysis. The astype method in pandas provides a simple and effective way to perform these conversions. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Understand Your Data: Know the formats and possible inconsistencies in your date strings.
- Use Explicit Formats: When possible, specify the date format to avoid ambiguity.
- Handle Missing Data: Use parameters like
errors='coerce'to handle missing or invalid data gracefully. - Optimize Performance: Be mindful of performance, especially with large datasets.
- Leverage Pandas Functions: Utilize pandas’ built-in functions like
pd.to_datetimeandinfer_datetime_format.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe