Pandas Where Function
The where function in Pandas is a powerful tool used to conditionally replace values in a DataFrame or Series. It is essential for data cleaning, transformation, and preparation tasks, making it a cornerstone function for data scientists and analysts working with Pandas. This article provides a detailed exploration of the where function, including its syntax, use cases, and practical examples with thorough explanations.
1. Introduction to Pandas Where Function
The where function is part of the Pandas library and is used to conditionally replace values in a DataFrame or Series. The basic idea is to replace values that do not satisfy a given condition with a specified value, typically NaN or another value of choice.
The syntax of the where function is as follows:
DataFrame.where(cond, other=nan, inplace=False, axis=None, level=None, errors='raise', try_cast=False)
cond: Condition to be checked. It can be a boolean array or a callable returning a boolean array.other: Value to replace where the condition isFalse. Default isnp.nan.inplace: IfTrue, do the operation in place and returnNone. Default isFalse.axis: Alignment axis if needed. Default isNone.level: Broadcast across a level, matching Index values on the passed MultiIndex level.errors: If ‘raise’, then raise a ValueError when the condition is not aligned with the input. Default is ‘raise’.try_cast: Try to cast the result back to the input type (if possible). Default isFalse.
2. Basic Usage
The basic usage of the where function involves replacing values in a Series or DataFrame based on a condition.
Example 1: Basic Usage with Series
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
result = s.where(s > 2, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, all values in the Series s that are not greater than 2 are replaced with the string ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 2: Basic Usage with DataFrame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
result = df.where(df > 2, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

Here, all values in the DataFrame df that are not greater than 2 are replaced with the string ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
3. Using where with DataFrames
When working with DataFrames, where can be used to conditionally replace values across the entire DataFrame or specific columns.
Example 3: Conditional Replacement Across DataFrame
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
result = df.where(df % 2 == 0, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:
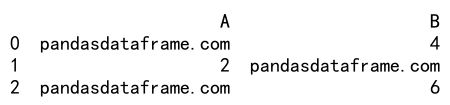
In this example, all odd values in the DataFrame df are replaced with the string ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 4: Conditional Replacement in Specific Column
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
df['A'] = df['A'].where(df['A'] > 2, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(df)
Output:

Here, only the values in column ‘A’ that are not greater than 2 are replaced with the string ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
4. Conditional Replacement with where
The where function is particularly useful for conditional replacement of values based on complex conditions.
Example 5: Using Multiple Conditions
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
condition = (df['A'] > 2) & (df['B'] < 6)
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, the values in the DataFrame df are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’ where column ‘A’ is not greater than 2 or column ‘B’ is not less than 6.
Example 6: Conditional Replacement with Different Values
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
condition = df['A'] > 2
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
result['B'] = df['B'].where(df['B'] < 6, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:
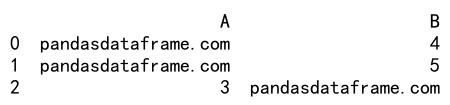
Here, values in column ‘A’ that are not greater than 2 are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’, and values in column ‘B’ that are not less than 6 are also replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
5. Combining Conditions
Combining multiple conditions can be achieved using logical operators such as & (and), | (or), and ~ (not).
Example 7: Combining Multiple Conditions
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'B': [5, 6, 7, 8]})
condition = (df['A'] > 1) & (df['B'] < 8)
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, values in the DataFrame df that do not satisfy the combined condition (df['A'] > 1) & (df['B'] < 8) are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
6. Using where with np.nan
The where function is commonly used to replace values with NaN.
Example 8: Replacing with NaN
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
result = df.where(df > 2)
print(result)
Output:
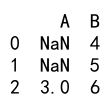
Here, values in the DataFrame df that are not greater than 2 are replaced with NaN.
7. Complex Conditions
Using complex conditions allows for more advanced data manipulation.
Example 10: Complex Condition with Multiple Columns
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'B': [5, 6, 7, 8]})
condition = (df['A'] + df['B'] > 7) | (df['A'] % 2 == 0)
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

Here, values in the DataFrame df that do not satisfy the complex condition (df['A'] + df['B'] > 7) | (df['A'] % 2 == 0) are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
8. Using where with Strings
The where function can also be applied to DataFrames containing strings.
Example 10: Conditional Replacement in String Columns
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'], 'B': ['one', 'two', 'three']})
result = df.where(df != 'foo', 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, values in the DataFrame df that are ‘foo’ are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 11: Using where with String Conditions
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'], 'B': ['one', 'two', 'three']})
condition = df['A'].str.contains('a')
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:
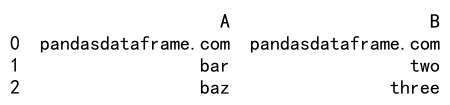
Here, values in the DataFrame df that do not contain ‘a’ in column ‘A’ are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
9. Practical Examples
This section provides more practical examples to illustrate the versatility of the where function.
Example 12: Using where with Custom Functions
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
condition = df.apply(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
result = df.where(condition, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:
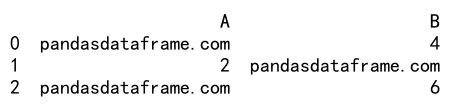
In this example, odd values in the DataFrame df are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’ using a custom function.
Example 13: Conditional Replacement Based on Multiple DataFrames
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'A': [0, 2, 4], 'B': [3, 5, 7]})
result = df1.where(df1 > df2, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:
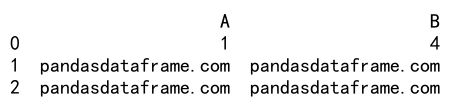
Here, values in df1 that are not greater than corresponding values in df2 are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 14: Using where with Grouped Data
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': ['foo', 'foo', 'bar'], 'B': [1, 2, 3]})
grouped = df.groupby('A')
result = grouped.transform(lambda x: x.where(x > 1, 'pandasdataframe.com'))
print(result)
Output:
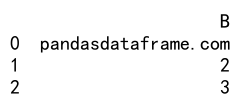
In this example, values in the grouped DataFrame df that are not greater than 1 are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 15: Applying where with iloc
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'B': [5, 6, 7, 8]})
result = df.where(df.iloc[:, 1] > 6, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

Here, values in the DataFrame df where the second column values are not greater than 6 are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
Example 16: Conditional Replacement with MultiIndex
import pandas as pd
arrays = [['bar', 'bar', 'baz', 'baz'], ['one', 'two', 'one', 'two']]
index = pd.MultiIndex.from_arrays(arrays, names=('first', 'second'))
df = pd.DataFrame({'A': [1, 2, 3, 4], 'B': [5, 6, 7, 8]}, index=index)
result = df.where(df['A'] > 2, 'pandasdataframe.com')
print(result)
Output:

In this example, values in the MultiIndex DataFrame df where column ‘A’ values are not greater than 2 are replaced with ‘pandasdataframe.com’.
 Pandas Dataframe
Pandas Dataframe